New insights into acute ischemic stroke from the perspective of spatial omics
- PMID: 40756344
- PMCID: PMC12316105
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.113396
New insights into acute ischemic stroke from the perspective of spatial omics
Abstract
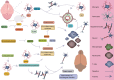
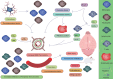
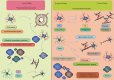
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a common cerebrovascular disease characterized by high incidence and disability rates, placing a significant burden on global healthcare systems. Various cell types, including microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and peripheral immune cells, interact in the pathological process of AIS, profoundly influencing the disease's prognosis. This review, for the first time, summarizes the biological functions and interaction mechanisms of microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, their subgroups, and infiltrating peripheral immune cells at different time points and spatial distributions following AIS, from the perspective of spatial single-cell omics. Spatial transcriptomics technology combines high-resolution gene expression information with tissue spatial architecture, enabling researchers to precisely identify the spatial distribution and dynamic crosstalk between CNS-resident cells and peripheral immune cell subsets. Intervening in the interactions between cell subgroups or different cell types and effectively targeting specific subgroups in the target area, may help minimize the negative effects of harmful subsets while enhancing the functions of beneficial ones. The application of spatial single-cell transcriptomics provides an unprecedented perspective for understanding the complex intercellular interactions following stroke, laying the foundation for precision interventions and targeted therapies.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; immune inflammation.; microglia; peripheral immune cells; spatial omics.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures







References
-
- Ban W, Jiang X, Lv L, Jiao Y, Huang J, Yang Z. et al. Illustrate the distribution and metabolic regulatory effects of pterostilbene in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rat brain by mass spectrometry imaging and spatial metabolomics. Talanta. 2024;266:125060. - PubMed
-
- Daniele SG, Trummer G, Hossmann KA, Vrselja Z, Benk C, Gobeske KT. et al. Brain vulnerability and viability after ischaemia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021;22:553–72. - PubMed
-
- Brouns R, De Deyn PP. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009;111:483–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

