Artemisiae Annuae Herba: from anti-malarial legacy to emerging anti-cancer potential
- PMID: 40756346
- PMCID: PMC12315818
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.115414
Artemisiae Annuae Herba: from anti-malarial legacy to emerging anti-cancer potential
Abstract
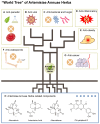
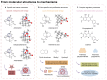
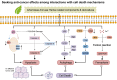
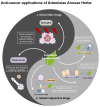
Modern medical approaches to cancer treatment face significant obstacles, including limited therapeutic options, narrow drug applicability, and rapid development of drug resistance. Consequently, re-evaluating traditional medicinal plants and natural compounds has emerged as a promising strategy to address this public health issue, particularly amid challenges in developing novel pharmaceuticals. Artemisiae Annuae Herba, a versatile natural drug renowned for its established efficacy against malaria and for other diverse pharmacological activities, is gaining recognition for its anti-cancer potential due to the unique structures and biological effects of its constituents. This review comprehensively outlines the major components of Artemisiae Annuae Herba and their reported anti-cancer activities, beginning with an examination of the molecular structures of the foundational components and an exploration of derivatives of these compounds. Furthermore, through an analysis of observed pharmacological effects, we systematically elucidate the multifaceted influence of Artemisiae Annuae Herba on cancerous tissues, including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, non-apoptotic cell death induction, angiogenesis inhibition, tumor microenvironment remodeling, and immune modulation. Finally, we discuss the feasibility of Artemisiae Annuae Herba in cancer therapy as well as the challenges and unresolved issues that require further investigation. We also consider ways that new drug formulations and routes of administration might overcome these translational hurdles. By synthesizing existing research on applications of Artemisiae Annuae Herba to cancer therapy, this review underscores potentially innovative clinical approaches, ultimately paving the way for the discovery of effective anti-cancer drugs with far-reaching benefits.
Keywords: Artemisiae Annuae Herba; cancer; derivatives; malaria; traditional Chinese medicine.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rabdosia rubescens (Hemsl.) H. Hara: A potent anti-tumor herbal remedy - Botany, phytochemistry, and clinical applications and insights.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;340:119200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119200. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39631716
-
[Research advances of biosynthesis, in vivo analysis and pharmacokinetics of chemical constituents in Artemisiae Annuae Herba].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jan;46(2):347-358. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200610.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33645121 Chinese.
-
[Review on study of Dao-di herbs Artemisiae Annuae Herba].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;41(11):2015-2018. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20161107. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28901094 Review. Chinese.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Yao CL, Zhang JQ, Li JY, Wei WL, Wu SF, Guo DA. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as a source of new anticancer drugs. Nat Prod Rep. 2021;38:1618–33. - PubMed
-
- Sui XB, Xie T. Combination of Chinese and Western medicine to prevent and reverse resistance of cancer cells to anticancer drugs. Chin J Integr Med. 2020;26:251–5. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Feiyue Z, Gaofeng L. Traditional Chinese medicine and lung cancer-From theory to practice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111381. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Qiu H, Li C, Cai P, Qi F. The positive role of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for cancer. Biosci Trends. 2021;15:283–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

