Epilepsy in MS and its association with cognitive and psychological burden
- PMID: 40756529
- PMCID: PMC12317197
- DOI: 10.1177/20552173251359061
Epilepsy in MS and its association with cognitive and psychological burden
Abstract
Background: Epilepsy is two to three times more common in patients with multiple sclerosis (pwMS) compared to the general population. Patients with MS and epilepsy without other identifiable causes (MS + E) show greater cortical damage than those without epilepsy (MS-E). However, it's unclear whether MS + E patients exhibit distinct cognitive and neuropsychological features requiring specific management.
Methods: In a cohort of pwMS from three MS centers, MS + E patients were identified and data on MS clinical features, epilepsy history, and treatments were collected. A matched group of MS-E patients was included. Assessments included cognitive and neuropsychiatric tests. Cognitive impairment (CI) was defined as scoring ≥1.5 standard deviations below normative values in ≥1 cognitive domain.
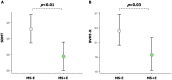
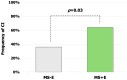
Results: CI was more prevalent in MS + E (n = 33) patients than in MS-E (n = 33). MS + E patients had lower processing speed (p < 0.01) and visuospatial memory (p = 0.03). MS + E was independently associated with CI (odds ratio 3.6, 95% confidence interval 1.21-12). Somatization, phobia, anxiety, and depression were the most affected neuropsychological domains in MS + E, with global psychological distress negatively correlating with processing speed (rho -0.36, p = 0.048).
Conclusions: MS + E is associated with higher CI, particularly in processing speed and visuospatial memory, alongside psychological distress, highlighting the need for targeted multidisciplinary care to improve outcomes and quality of life.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis; cognitive impairment; damage; epilepsy; neuropsychological dysfunction; seizure.
© The Author(s), 2025.
Figures

References
-
- Kuntz S, Wu AS, Matheson E, et al. Association between multiple sclerosis and epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2023; 69: 104421. - PubMed
-
- Dagiasi I, Vall V, Kumlien E, et al. Treatment of epilepsy in multiple sclerosis. Seizure 2018; 58: 47–51. - PubMed
-
- Striano P, Striano S, Carrieri PBet al. et al. Epilepsia partialis continua as a first symptom of multiple sclerosis: electrophysiological study of one case. Mult Scler 2003; 9: 199–203. - PubMed
-
- Burman J, Zelano J. Epilepsy in multiple sclerosis: a nationwide population-based register study. Neurology 2017; 89: 2462–2468. - PubMed
-
- Pozzilli V, Haggiag S, Di Filippo M, et al. Incidence and determinants of seizures in multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2024; 95: 612–619. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

