Emerging Use of BPC-157 in Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40756949
- PMCID: PMC12313605
- DOI: 10.1177/15563316251355551
Emerging Use of BPC-157 in Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: A Systematic Review
Abstract
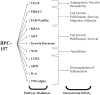
Background: Body protection compound-157 (BPC-157) is a naturally occurring gastric peptide that promotes mucosal integrity and homeostasis. Preclinical studies show its potential for promoting healing in musculoskeletal injuries such as fractures, tendon ruptures, ligament tears, and muscle injuries. Despite lacking US Food and Drug Administration approval and its use being banned in professional sports, it is increasingly used by clinicians and athletes. Purpose: We sought to (1) provide a comprehensive synthesis of the BPC-157 literature from an orthopedic sports medicine perspective and (2) elucidate the mechanism of action, musculoskeletal effects, metabolism, and safety profile. Methods. We conducted a systematic review of English-language literature, published from database inception to June 3, 2024, from PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase. We searched PROSPERO to identify any current or unpublished reviews. Studies reporting BPC-157's mechanism, musculoskeletal outcomes, metabolism, and safety were included. Articles were screened in 3 phases by 2 reviewers. In cases of a disagreement between the 2 reviewers, blinding was removed, and eligibility was determined by group consensus, with a third author making the final decision. Results. A total of 544 articles from 1993 to 2024 were identified. After duplicates were removed, 36 studies were included (35 preclinical studies, 1 clinical study). The studies suggest that BPC-157 enhances growth hormone receptor expression and several pathways involved in cell growth and angiogenesis, while reducing inflammatory cytokines. In preclinical models, BPC-157 improved functional, structural, and biomechanical outcomes in muscle, tendon, ligament, and bony injuries. In a retrospective study of musculoskeletal pain following intraarticular injection of BPC-157 for unspecified chronic knee pain, 7 of 12 patients reported relief for >6 months. BPC-157 is metabolized in the liver, with a half-life of less than 30 minutes, and is cleared by the kidneys. Preclinical safety studies showed no adverse effects across several organ systems. No clinical safety data were found. Conclusion: This systematic review of level IV and level V studies suggests that BPC-157 shows promise for promoting recovery from musculoskeletal injuries. Adverse effects are possible due to unregulated manufacturing, contamination, or unknown clinical safety. We recommend that clinicians counsel athletes to understand their organizations' rules to remain compliant with medication/supplement safety and testing standards.
Keywords: BPC-157; athlete; body protection compound-157; gastric pentadecapeptide; orthobiologics; peptide; sports.
Plain language summary
Review of the Musculoskeletal Literature Surrounding a Relatively Novel Peptide, Body Protection Compound-157 Body protection compound-157 (BPC-157) is a naturally occurring substance in the body that helps maintain healthy tissues and organs. Even though it is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and is banned in some sports, BPC-157 is still being used. This study aimed to review all the research on BPC-157 to understand how it works, its effects on muscles and joints, how the body processes it, and whether it is safe. The review looked at 36 studies published from 1993 to 2024. The findings showed that BPC-157 helps promote healing by boosting growth factors and reducing inflammation. It has improved outcomes in muscle, tendon, ligament, and bone injury models in animals. In one human study, 7 out of 12 people with chronic knee pain felt relief for over six months after receiving one BPC-157 knee injection. Animal studies showed no harmful effects, but there is no clinical safety data in humans. Overall, BPC-157 could help heal musculoskeletal injuries, but there are potential risks due to unregulated production and lack of clinical safety data.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Michael J. Salata, MD, declares a relationship with Stryker. Michael Karns, MD, declares relationships with Smith & Nephew and Arthrex. Jacob G. Calcei, MD, declares a relationship with Smith & Nephew. James E. Voos, MD, declares relationships with Arthrex and Mitek. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brcic L, Brcic I, Staresinic M, Novinscak T, Sikiric P, Seiwerth S. Modulatory effect of gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on angiogenesis in muscle and tendon healing. J Physiol Pharmacol Off J Pol Physiol Soc. 2009;60(Suppl 7):191–196. - PubMed
-
- Cameron D, Burger H, Catt C, Gordon E, Watts J. Metabolic clearance of human growth hormone in patients with hepatic and renal failure, and in the isolated perfused pig liver. Metabolism. 1972;21(10):895–904. - PubMed
-
- Cerovecki T, Bojanic I, Brcic L, et al. Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 (PL 14736) improves ligament healing in the rat. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:1155–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

