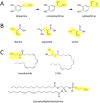
Several endocannabinoids and amino acids may be biosynthetically converted to catecholamines in vivo
- PMID: 40756988
- PMCID: PMC12314285
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1614460
Several endocannabinoids and amino acids may be biosynthetically converted to catecholamines in vivo
Keywords: adrenaline; dopamine; epinephrine; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; noradrenaline; norepinephrine; stable isotope.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Level of urinary catecholamine in children with Sleep Disordered Breathing: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Sleep Med. 2022 Dec;100:565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2022.10.008. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 36327585
-
Adrenaline for prevention of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants with cardiovascular compromise.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;2004(1):CD003958. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003958.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. PMID: 14974048 Free PMC article.
-
[Urinary excretion of the catecholamines adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine as well as the derivatives metanephrine and normetanephrine in heart disease patients].Z Kardiol. 1976 Dec;65(12):1124-38. Z Kardiol. 1976. PMID: 1014804 German.
-
Many Drugs of Abuse May Be Acutely Transformed to Dopamine, Norepinephrine and Epinephrine In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10706. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910706. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catecholamines for shock: the quest for high-quality evidence.Crit Care Resusc. 2007 Dec;9(4):352-6. Crit Care Resusc. 2007. PMID: 18052900
References
-
- Castelli V., Lavanco G., D’Amico C., Feo S., Tringali G., Kuchar M., et al. (2023). CBD enhances the cognitive score of adolescent rats prenatally exposed to THC and fine-tunes relevant effectors of hippocampal plasticity. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1237485. 10.3389/fphar.2023.1237485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

