Revolutionizing rheumatoid arthritis therapy: the potential of lipid nanocarriers
- PMID: 40757154
- PMCID: PMC12314878
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra04258e
Revolutionizing rheumatoid arthritis therapy: the potential of lipid nanocarriers
Abstract
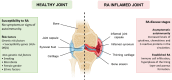
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by synovitis, systemic inflammation and autoantibodies, leading to joint damage and disability. RA pathogenesis is characterized by a dysregulated interaction between immune cells, particularly B cells and T cells, which release inflammatory cytokines. This review explores the pivotal role of these immune cells in sustaining the inflammatory response and contributing to tissue injury. We provide a comprehensive overview of current RA therapies, highlighting the limitations of conventional treatments and the pressing need for targeted drug delivery systems such as lipid nanocarrier-based therapies, including nano-emulsions, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), niosomes, liposomes, transferosomes, and ethosomes. Emphasizing niosomes, we discuss their capacity to encapsulate multiple drugs, significantly enhancing bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. By directing drug-loaded niosomes to inflamed synovial sites, this innovative approach minimizes systemic side effects while maximizing localized drug concentrations, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes for RA patients. This review underscores the importance of targeted (nano)drug delivery in improving patient's life quality and represents a significant step toward more effective, personalized RA therapies by deepening our understanding of the underlying mechanisms.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
DS-Modified Paeoniflorin pH-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Macrophage Polarization in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 12;20:8967-8992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S516434. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40671689 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Phytochemical-based Nanocarrier Approaches for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Challenges and Scope for Future-generation Formulations.Recent Adv Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2025;19(2):189-212. doi: 10.2174/0127722708304673240903184606. Recent Adv Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40667594 Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers as a Promising Delivery System in the Management of Acne.Curr Pharm Des. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.2174/0113816128404408250707111455. Online ahead of print. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 40685735
-
Recent Advancement in Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.2174/0115701638376838250701221200. Online ahead of print. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025. PMID: 40660434
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Global RA Network, 2021, https://globalranetwork.org/project/disease-info/
-
- Senthelal S., Li J., Ardeshirzadeh S. and Thomas M. A., Arthritis, StatPearls Publishing, 2023 - PubMed
-
- Poudel P., Goyal A. and Lappin S. L., Inflammatory Arthritis, StatPearls Publishing, 2023 - PubMed
-
- Weyand C. M. Goronzy J. J. Med. Clin. North Am. 1997;81(1):29–55. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

