Nursing care for a patient with intracerebral hemorrhage complicated with toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case report
- PMID: 40757201
- PMCID: PMC12313555
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1587979
Nursing care for a patient with intracerebral hemorrhage complicated with toxic epidermal necrolysis: a case report
Abstract
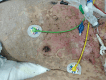
This study summarizes the nursing care for a patient with intracerebral hemorrhage complicated with toxic epidermal necrolysis, focusing on infection prevention and control. Advanced health assessment showed that the primary nursing issue was a high risk of infection. Nursing interventions were implemented to prevent and control infection in various systems, emphasizing four key aspects: respiratory management after tracheostomy, lumbar cistern drainage care, skin management, and nutritional support. The patient's skin healed, infection indicators decreased, and no secondary infections occurred. On the 24 th day after admission, the patient was transferred to the neurosurgery department for ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery. The patient was transferred to a rehabilitation hospital 21 days after surgery.
Keywords: infection; intracerebral hemorrhage; lumbar cistern drainage; nursing; toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Li, Lai and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Heuer R, Paulmann M, Annecke T, Behr B, Boch K, Boos A, et al. S3 Guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis) - part 1: Diagnosis, initial management, and immunomodulating systemic therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. (2024) 22:1448–66. 10.1111/ddg.15515 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paulmann M, Heuer R, Annecke T, Behr B, Boch K, Boos A, et al. S3 Guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis) - Part 2: Supportive therapy of en in the acute and post-acute stages. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. (2024) 22:1576–93. 10.1111/ddg.15516 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao L, Liu Y, Jiang Q, Cai L. Nursing care of a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome. Zhonghua Hu Li Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Nursing]. (2023) 58:1629–34. 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.13.015 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources