A SARM a Day Keeps the Weakness Away: A Computational Approach for Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) and Their Interactions with Androgen Receptor and 5‑Alpha Reductase Proteins
- PMID: 40757306
- PMCID: PMC12311730
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02504
A SARM a Day Keeps the Weakness Away: A Computational Approach for Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) and Their Interactions with Androgen Receptor and 5‑Alpha Reductase Proteins
Abstract
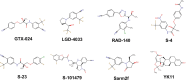
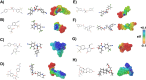
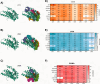
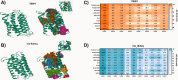
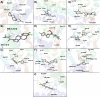
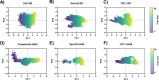
This study examines the molecular interactions of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) with the androgen receptor (AR) and 5-alpha reductase II (5αRII), highlighting their potential as dual-action pharmacological candidates, using molecular modeling techniques to evaluate their primary interactions, providing valuable insights into conformational stability and ligand-induced changes and enabling rational analysis of SARMs with optimized pharmacological profiles. Employing molecular docking, density functional theory (DFT), and molecular dynamics simulations, we analyzed the binding affinities and conformational stability. Between all eight SARMs tested, 4'-[(2S,3S)-2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-5-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl]-2'-(trifluoromethyl)-benzonitrile (Sarm2f) demonstrated exceptional stability and binding affinity with critical interactions at key AR residues such as Asn705, Glu711, Arg752, and Thr877. The inclusion of fluorinated groups enhances hydrogen bonding through dipole induction, improving the binding dynamics. Additionally, Sarm2f interacts with small hydrophobic pockets around the 5-oxopyrrolidine ring, further stabilizing its conformation. Also, (17α,20E)-17,20-[(1-methoxyethylidene)-bis-(oxy)]-3-oxo-19-norpregna-4,20-diene-21-carboxylic acid methyl ester (YK11) exhibited compelling interactions with both AR and 5αRII, characterized by a tetracyclic steroidal nucleus that enhances its androgenic activity. Structural modifications, including a double bond at the C20 position in YK11, improve stability and prolong interactions with the AR. While Sarm2f shows lower root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) values, indicating rigidity, the slight flexibility of YK11 may allow for a broader range of interactions. These findings emphasize the importance of advanced computational methods in optimizing SARMs by demonstrating how specific chemical modifications affect binding affinity and selectivity for AR and 5αRII, thereby aiding the development of safer and more effective pharmacological agents for androgen-related conditions.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures



References
-
- Leciejewska N., Jędrejko K., Gómez-Renaud V. M., Manríquez-Núñez J., Muszyn’ska B., Pokrywka A.. Selective androgen receptor modulator use and related adverse events including drug-induced liver injury: analysis of suspected cases. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024;80(2):185–202. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03592-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
