Real-world assessment of clinical outcomes of first-line treatment in metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40757924
- PMCID: PMC12445671
- DOI: 10.1093/oncolo/oyaf240
Real-world assessment of clinical outcomes of first-line treatment in metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the most common non-clear cell RCC (nccRCC), representing up to 15% of RCC cases. Phase 2 trials have evaluated first-line (1L) immunotherapy (IO)-based treatment in nccRCC, but with heterogeneous cohorts and limited comparative data. The specific value of IO for metastatic pRCC (mpRCC) remains unquantified.
Methods: We analyzed prospectively collected data from the Canadian Kidney Cancer Information System to assess the efficacy of 1L systemic therapy in mpRCC with IO-based regimens vs tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). The primary endpoint was time-to-treatment failure (TTF). Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs). Analyses were adjusted (adj) for IMDC risk groups.
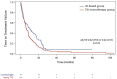
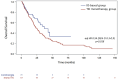
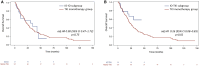
Results: From 2011 to 2024, 197 mpRCC patients received 1L therapy: 70 with IO (alone or in combination) and 127 with TKI. Median follow-up was 21.6 months. Median TTF was 9.9 months with IO vs 5.9 months with TKI (adjHR: 0.62 [0.43-0.91], P = .01). Median OS was 36.9 months with IO vs 23.2 months with TKI (adjHR: 0.54 [0.3-0.9], P = .018). Objective response rate was 37% with IO vs 23% with TKI (adjOR: 2.2 [0.95-5.2], P = .07). The TKI-IO subgroup showed the longest TTF (16.9 months, adjHR: 0.47 [0.26-0.85], P = .01) and OS (not reached, adjHR: 0.26 [0.08-0.83], P = .02), compared to TKI. Grade 3-5 TRAEs occurred in 31% (IO) vs 27% (TKI).
Conclusions: This real-world study highlights the benefit of IO-based treatment in mpRCC, particularly in the TKI-IO subgroup. Our findings may inform further trials evaluating 1L IO in mpRCC.
Keywords: CKCis; TKI; first-line systemic treatment; immunotherapy; metastatic papillary renal-cell cancer.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.V.-B.: consulting: AstraZeneca, BMS/travel: AstraZeneca.
Z.H.: None.
S.G.: None.
D.Y.C.H.: Consulting: Pfizer, Novartis, BMS, Janssen, Astellas pharma, Ipsen, Eisai, Merck/Research funding for his institution: Pfizer, Exelixis, Novartis, BMS, Ipsen.
L.A.W.: Research funding for her institution: BMS, Pfizer, Roche Canada, Merck, AstraZeneca.
N.S.B.: Consulting: Pfizer, BMS, Janssen, Astellas pharma, Ipsen, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Merck, Bayer, EMD Serono, Seagen/Travel: Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen, Pfizer/Honoraria: Pfizer, Janssen, Astellas pharma, Ipsen, AstraZeneca, Eisai, Merck, Bayer, Seagen, Takeda/Research funding for his institution: Ipsen/Stock ownership: illumiSonics.
C.K.K.: Consulting: Pfizer, BMS, Janssen, Astellas pharma, Eisai, Merck, Bayer, Seagen, AAA-Novartis, Gilead sciences, Ipsen/Travel: Ipsen, AAA Canada, Pfizer, Janssen/Honoraria: Pfizer, BMS, Janssen, Ipsen, Merck, Astellas pharma, Eisai, Seagen, Bayer.
J.G.: Consulting: Janssen, Ipsen, AstraZeneca, Merck, EMD Serono/Honoraria: Ipsen, Pfizer, Merck, Janssen.
B.B.: Consulting: Janssen, Bayer, Ferring, Verity Pharmaceuticals/Honoraria: Merck, Bayer.
A.F.: Consulting: Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Bayer, AbbVie, TerSera/Honoraria: Amgen, Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Bayer, AbbVie, TerSera, Merck/Stock ownership: AbbVie, Medtronic.
G.A.B.: Consulting: Pfizer, BMS, Eisai, Ipsen/Honoraria: Pfizer, BMS, Eisai, Ipsen, Merck/Research funding for his institution: Pfizer, Merck.
D.B.: Consulting: BMS, AbbVie, Pfizer, Bayer, Ipsen, AstraZeneca, Merck, Astellas pharma, Knight Therapeutics/Travel: Knight Therapeutics, Ipsen, Janssen, EMD Serono/Honoraria: Amgen, Ipsen, Janssen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Pfizer, Eisai, Bayer, Merck, EMD Serono/Research funding: Ipsen.
F.P.: Consulting: Astellas pharma, Bayer, Janssen, Tolmar, TerSera, Merck, AstraZeneca/Speakers’ Bureau: Bayer, Astellas pharma, Janssen, Novartis/Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property/Stock ownership: Allogene Therapeutics/Honoraria: Astellas pharma, Janssen, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Tolmar, Novartis, TerSera/Research funding for his institution: Astellas pharma, TerSera, Janssen, Merck, Novartis.
V.C.: Consulting: AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen, Janssen, Eisai, Pfizer, Astellas pharma, Merck, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline Canada/Research funding for his institution: Merck, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS.
R.H.B.: None.
R.R.S.: None.
E.W.: Consulting: Merck, Bayer, Roche, Eisai, Ipsen, EMD Serono/Research funding for his institution: Merck, Novartis, Lilly.
A.-K.A.L.: Consulting: Eisai, Merck, Ipsen, Pfizer, BMS, AbbVie, Janssen, Bayer, Astellas pharma, Novartis/Honoraria: Pfizer, Roche, Merck, Novartis, Astellas pharma, Bayer, BMS, Eisai, Ipsen/Research funding for his institution: BMS, Novartis, Roche, Ipsen, EMD Serono, BioCanRx.
D.S.: Consulting: Merck, Pfizer, Ipsen, Adlai Nortye, Eisai/Honoraria: Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, BMS, Ipsen, Eisai, Adlai Nortye, Bicara Therapeutics/Research funding for his institution: Novartis, Pfizer, Merck, Roche, BMS, Lilly, Adlai Nortye, GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures

References
-
- Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM, et al. The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs—part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2022;82:458-468. - PubMed
-
- Vera-Badillo FE, Templeton AJ, Duran I, et al. Systemic therapy for non–clear cell renal cell carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2015;67:740-749. - PubMed
-
- de Velasco G, McKay RR, Lin X, et al. Comprehensive analysis of survival outcomes in non–clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients treated in clinical trials. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15:652-660.e1. - PubMed
-
- Giles RH, Choueiri TK, Heng DY, et al. Recommendations for the management of rare kidney cancers. Eur Urol. 2017;72:974-983. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

