A nomogram model for predicting maternal cardiovascular complications and neonatal adverse outcomes in pregnant patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 40758664
- PMCID: PMC12322992
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2541093
A nomogram model for predicting maternal cardiovascular complications and neonatal adverse outcomes in pregnant patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) during pregnancy significantly increases maternal and fetal mortality risk. We developed nomogram prediction models from retrospective data to assess maternal cardiovascular risks and neonatal adverse outcomes.
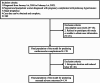
Methods: Our study included 170 pregnant women, divided into training (70%) and validation (30%) sets. Predictors of outcomes were identified using logistic regression in the training set, and nomograms were constructed to predict maternal cardiovascular complications and neonatal adverse outcomes. Model performance was evaluated through internal validation.
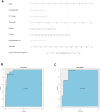
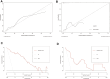
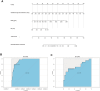
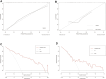
Results: Predictors of cardiovascular complications included severe PAH (OR = 4.80), New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification ≥ III (OR = 25.94), ST-T changes (OR = 25.18), total bilirubin (OR = 1.49), albumin (OR = 0.87) and lactate dehydrogenase level (OR = 1.01). The nomogram showed high predictive accuracy with concordance indices of 0.96 and 0.91, areas under the ROC curve of 0.96 and 0.93. Neonatal outcome predictors included gestational age at termination (OR: 0.93), maternal platelet count level (OR: 0.99), and B-type natriuretic peptide level (OR: 1.00). The corresponding nomogram showed concordance indices in the training set and validation set were 0.92 and 0.73, respectively, with area under the ROC curve values of 0.92 and 0.73.
Conclusions: Nomogram models based on the above factors useful tools for predicting cardiovascular complications and neonatal adverse outcomes in pregnant women with PAH, potentially aiding in early detection and timely intervention. Further validation is needed to confirm their accuracy in broader clinical settings.
Keywords: Pregnancy; maternal and neonatal outcomes; prediction model; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(1):67–119. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Regitz-Zagrosek V, Roos-Hesselink JW, Bauersachs J, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(18):1543–1562. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac287. - DOI
-
- Lewis GD, Bossone E, Naeije R, et al. Pulmonary vascular hemodynamic response to exercise in healthy adults and in pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2020;56(5):2000945. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00945-2020. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
