Harnessing BET-Bromodomain Assisted Nuclear Import for Targeted Subcellular Localization and Enhanced Efficacy of Antisense Oligonucleotides
- PMID: 40758869
- PMCID: PMC12356583
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c09544
Harnessing BET-Bromodomain Assisted Nuclear Import for Targeted Subcellular Localization and Enhanced Efficacy of Antisense Oligonucleotides
Abstract
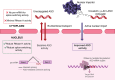
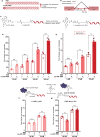
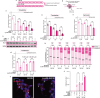
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are a promising class of therapeutics designed to modulate gene expression. Both key mechanisms of action for ASOs operate in the nucleus: splice-switching ASOs modify pre-mRNA, processed in the nucleus, and mRNA-degrading ASOs require RNase H, an enzyme predominantly active in the nucleus. Therefore, to achieve maximal therapeutic efficacy, ASOs require efficient nuclear delivery. In this work, we have synthesized ASO conjugates for active nuclear import, by covalent conjugation with a potent and proven small-molecule nuclear importer, (+)-JQ1. (+)-JQ1 is a well-characterized high-affinity binder for members of the BET bromodomain family of proteins and was recently shown to transport cytoplasmic proteins into the nucleus. Our (+)-JQ1-ASO conjugates outperformed their unmodified counterparts for both splice-switching and mRNA knockdown in the nucleus, across different molecular targets, backbone chemistries, and cell lines. In addition, we show that the improvement in on-target efficacy correlates with increased nuclear localization of the (+)-JQ1-modified ASOs by subcellular fractionation and immunocytochemistry. Notably, we improved the performance of Oblimersen, a BCL-2 ASO drug that failed in phase-III clinical trials. (+)-JQ1-Oblimersen showed increased effectiveness in an acute myeloid leukemia cell model, showing that this therapeutic may merit re-evaluation. This work demonstrates that the covalent modification of ASOs with a small-molecule nuclear importer can significantly improve target engagement and pave the way for more effective therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Engineering antisense oligonucleotides for targeted mRNA degradation through lysosomal trafficking.Chem Sci. 2025 Jun 9;16(28):13096-13105. doi: 10.1039/d5sc03751d. eCollection 2025 Jul 16. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40547092 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying antisense oligonucleotides for targeted inhibition of insulin receptor isoform A.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 15;15:1563985. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1563985. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40303997 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

