Lesser-known non-apoptotic programmed cell death in viral infections
- PMID: 40759382
- PMCID: PMC12357283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2025.199612
Lesser-known non-apoptotic programmed cell death in viral infections
Abstract
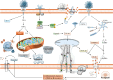
Non-apoptotic programmed cell death (NAPCD) represents a diverse set of cell death mechanisms that differ from classical apoptosis and have recently gained attention in the context of viral infections. This review focuses on four key NAPCD types, including ferroptosis, cuproptosis, NETosis (neutrophil extracellular trap formation), and PANoptosis (a combination of pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis), and summarizes their distinct molecular pathways and roles during viral infections. We emphasize their functional relevance in SARS-CoV-2 infection, revealing how they significantly impact viral replication, host immune responses, and tissue damage. Furthermore, we explore the interaction between NAPCDs and specific immune responses. Specifically, ferroptosis influences macrophage polarization. Cuproptosis activates innate immunity via the cGAS-STING pathway. NETosis contributes to Th17 responses, and PANoptosis interacts with Th1, Th22, and Thαβ pathways. Understanding the interplay among these cell death pathways provides new insights into host-virus dynamics and uncovers potential therapeutic targets for viral diseases.
Keywords: Cuproptosis; Ferroptosis; NAPCD; NETosis; PANoptosis.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Programmed cell death in paramyxovirus infection].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 May 25;54(3):399-410. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2024-0512. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40394914 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Multiple cell death modalities and immune response in pulpitis.Int Endod J. 2025 Jan;58(1):111-127. doi: 10.1111/iej.14145. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Int Endod J. 2025. PMID: 39257034
-
Ferroptosis and mitochondrial ROS are central to SARS-CoV-2-induced hepatocyte death.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Aug 11;15:1625928. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1625928. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40861496 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and pyroptosis in the nasal mucosa of Syrian hamster during SARS-CoV-2 infection and reinfection.Apoptosis. 2024 Aug;29(7-8):1246-1259. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01940-x. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38416286
-
p53-regulated non-apoptotic cell death pathways and their relevance in cancer and other diseases.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Aug;26(8):600-614. doi: 10.1038/s41580-025-00842-3. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40204927 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

