Defective Olfactomedin-2 connects adipocyte dysfunction to obesity
- PMID: 40759652
- PMCID: PMC12322249
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62430-5
Defective Olfactomedin-2 connects adipocyte dysfunction to obesity
Abstract
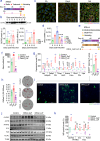
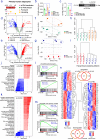
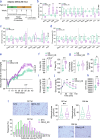
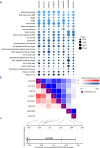
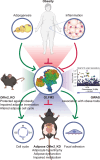
Olfactomedin-2 (OLFM2) is a pleiotropic glycoprotein emerging as a regulator of energy homeostasis. We here show the expression of OLFM2 to be adipocyte-specific and inversely associated with obesity. OLFM2 levels increase during adipogenesis and are suppressed in inflamed adipocytes. Functionally, OLFM2 deficiency impairs adipocyte differentiation, while its over-production enhances the adipogenic transformation of fat cell progenitors. Loss and gain of function experiments revealed that OLFM2 modulates key metabolic and structural pathways, including PPAR signaling, citrate cycle, fatty acid degradation, axon guidance and focal adhesion in 3T3 cell lines and primary human adipocytes. On the molecular level, OLFM2 deficiency in differentiated adipocytes predominantly downregulates genes involved in cell cycle. Extending these findings in vivo, both whole-body Olfm2 knockout and adipose-specific Olfm2 depletion in mice resulted in impaired adipose cell cycle gene expression, with the latter also displaying fat mass accretion and metabolic dysfunction. Collectively, our results underscore a critical role for OLFM2 in adipocyte biology, and support a causative link between reduced adipose OLFM2 and the pathophysiology of obesity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have nothing to disclose. All authors have approved the final version submitted, being listed as authors on the manuscript. The contents of this manuscript have not been copyrighted or published previously. The contents of this manuscript are not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Figures




References
-
- Stankiewicz, T. R., Gray, J. J., Winter, A. N. & Linseman, D. A. C-terminal binding proteins: central players in development and disease. Biomol. Concepts5, 489–511 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Li, Q., Liu, A., Gu, X. & Su, Z. Olfactomedin domain-containing proteins: evolution, functional divergence, expression patterns and damaging SNPs. Mol. Genet. Genom.294, 875–885 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Zeng, L. C., Han, Z. G. & Ma, W. J. Elucidation of subfamily segregation and intramolecular coevolution of the olfactomedin-like proteins by comprehensive phylogenetic analysis and gene expression pattern assessment. FEBS Lett.579, 5443–5453 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

