The efficacy of the three-port bimanual technique for direct perfluorocarbon liquid-silicone oil exchange in vitrectomy for the treatment of advanced proliferative vitreoretinopathy
- PMID: 40759944
- PMCID: PMC12323066
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04281-8
The efficacy of the three-port bimanual technique for direct perfluorocarbon liquid-silicone oil exchange in vitrectomy for the treatment of advanced proliferative vitreoretinopathy
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of three-port, bimanual technique for direct perfluorocarbon liquid (PFCL)-silicone oil (SO) exchange in avoiding retinal re-detachment and shortening the surgical duration in 23-gauge (23 G) pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) for the treatment of advanced proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) complicating primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD).
Methods: A Retrospective, comparative, consecutive, single-center study was conducted. Fifty-one eyes of 51 patients diagnosed with RRD complicated by PVR at the severe C stage, according to the standardized grading system, were retrospectively reviewed over a 3-year period. All patients underwent three-port 23 G PPV following a standardized protocol. Twenty-three eyes underwent the bimanual technique for direct PFCL-SO exchange during the final surgical steps, while twenty-eight eyes received conventional air-fluid exchange (AFE) for PFCL removal before SO tamponade. Primary outcome measures included visual acuity (logMAR), retinal status, intraocular pressure (IOP), surgical time and incidence of intraoperative and postoperative complications over a minimum 12-month follow-up period.
Results: The primary anatomical success rate was 86.9% in the bimanual group versus 85.7% in the AFE group (P = 0.898). Visual acuity on postoperative day 1 was significantly improved in the bimanual group compared with the AFE group (P = 0.022). The surgical duration of bimanual group was significantly reduced compared to that of AFE group (P < 0.001). Two eyes in AFE group developed intraocular lens decentration during the surgical procedure. No statistically significant differences were observed in the incidence of postoperative complications between groups.
Conclusion: The bimanual technique for direct PFCL-SO exchange is advantageous for enhancing the efficiency of surgical procedures, reducing the incidence of intraoperative complications and maintaining the re-flattened retina in the process of PFCL aspiration and SO injection. This novel approach presents a feasible and cost-effective strategy to enhance both operational efficiency and rapid visual rehabilitation in the immediate postoperative period.
Keywords: Bimanual technique; Pars plana vitrectomy; Perfluorocarbon liquid; Proliferative vitreoretinopathy; Retinal detachment; Silicone oil.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the The Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University Ethics Committee. Informed consent was obtained from all participants, and the study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


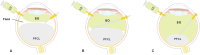
References
-
- Pastor JC. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: an overview. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998;43(1):3–18. - PubMed
-
- Baudouin C, Fredj-Reygrobellet D, Gordon WC, Baudouin F, Peyman G, Lapalus P, Gastaud P, Bazan NG. Immunohistologic study of epiretinal membranes in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990;110(6):593–8. - PubMed
-
- Pastor JC, de la Rua ER, Martin F. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: risk factors and pathobiology. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2002;21(1):127–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

