Caffeine-augmented exercise as a pretreatment for locomotor and balance impairments induced by REM sleep deprivation in rats
- PMID: 40760087
- PMCID: PMC12322054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13760-3
Caffeine-augmented exercise as a pretreatment for locomotor and balance impairments induced by REM sleep deprivation in rats
Abstract
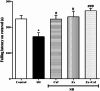
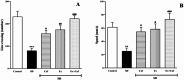
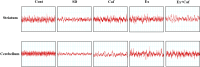
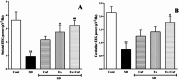
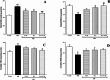
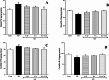
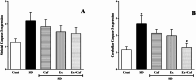
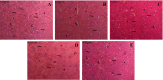
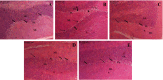
Sleep deprivation (SD) is a common problem that can lead to various neurological disorders. This study was carried out to examine how SD impacts locomotor performance and coordination in rats. Moreover, we aimed to investigate the potential synergistic benefits of caffeine supplementation coupled with treadmill exercise in mitigating any locomotor disorders induced by SD. Male rats were assigned to five groups: control, SD, SD + caffeine, SD + exercise, SD + caffeine + exercise. After 5 weeks of receiving caffeine supplementation (30 mg/kg) and/or treadmill exercise, the rats underwent 72 h of REM-SD, followed by behavioral tests. Subsequently, various analyses, including electrophysiology recordings, oxidative stress levels, neuroinflammation markers, apoptosis indicator, and histological changes were evaluated in the striatum and cerebellum. REM-SD significantly impaired motor and balance function, decreased neuronal activity, and increased oxidative stress, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers in the striatum and cerebellum. The study also found that REM-SD led to induce histopathological changes in these brain regions. Importantly, the administration of caffeine or regular exercise helped mitigate these adverse effects of REM-SD on motor, neuronal, molecular, and histological measures. Moreover, the combination of caffeine and exercise proved particularly effective, as it not only improved the motor and neuronal deficits, but also reduced the oxidative stress, inflammatory and apoptotic factors. The findings suggest that caffeine and exercise synergistically mitigate REM-SD-induced locomotor and neuronal deficits, particularly in locomotion and balance-related brain regions, potentially through reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Keywords: Caffeine; Cerebellum; Exercise; Locomotion; Sleep deprivation; Striatum.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caffeine and Exercise: A Dual Approach to Combat Cognitive Decline Induced by REM Sleep Deprivation.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):9625-9637. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04845-1. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40131698
-
Exploring Crocin's Role in Alleviating Memory Impairments and Depression-like Behaviors Induced by REM Sleep Deprivation, Focusing on BDNF and GSK-3β in Male Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):8638-8651. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04753-4. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40025325
-
Cardiovascular and neuroimmune adaptations to enalapril and exercise training: A comparative study in male and ovariectomized female spontaneously hypertensive rats.Auton Neurosci. 2025 Aug;260:103280. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2025.103280. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Auton Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40253895
-
Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 16;11(11):CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 15;11:CD009178. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub4. PMID: 27851868 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Micić, D. D. et al. Sleep and metabolic disorders. Glas. Srpska Akademija Nauka I Umetnosti. Odeljenje Medicinskih Nauka. 51, 5–25 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

