Identification of Novel Scaffolds Against GSK-3β for Targeting Alzheimer's Disease Through Molecular Modeling Techniques
- PMID: 40760108
- PMCID: PMC12321713
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-025-01568-8
Identification of Novel Scaffolds Against GSK-3β for Targeting Alzheimer's Disease Through Molecular Modeling Techniques
Abstract
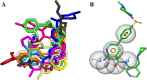
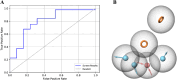
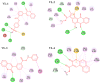
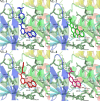
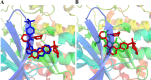
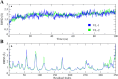
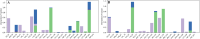
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common causes of dementia in elderly populations. A multifactorial and complex etiology has hindered the establishment of successful disease-modifying and retarding treatments. An important molecular target that has a close link with the disease's pathophysiology is glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β). GSK-3β is thought to be an important bridge between amyloid and tau pathologies, the two principle pathogenic hallmarks of the disease. In particular, its kinase activity is thought to be a contributing factor for initiating aberrant tau hyperphosphorylation toward neurodegenerative progression. To identify potential inhibitors for GSK-3β, a pharmacophore-based virtual screening was used on the VITAS-M Lab database, a large database of small molecules. A co-crystal ligand employed as the template allowed the screening of roughly 200,000 compounds. Compounds successfully screened were selected on the basis of the Phase screen score combining vector alignments, volume scores, and site matching parameters. Using a cutoff score of 1.7, 174 compounds were docked using the Glide tool for molecular docking to further identify potential high-affinity binding ligands. Finally, four chemicals with the best binding scores (cutoff Glide GScore values of - 8 kcal/mol) were identified. Among these, 3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)-N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl) benzamide (VL-1) and trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (VL-2) showed strong and stable binding interactions, as evidenced by molecular dynamics simulation (MDS). The results suggest that VL-1 and VL-2 may serve as promising lead compounds for GSK-3β-based anti-AD therapeutics. However, further in vivo mechanistic validation is warrantied to confirm their therapeutic applicability.
Keywords: ADMET; Alzheimer’s disease; Dementia; Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; Molecular simulation; Virtual screening.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. Ethical Approval: Not applicable, as no human or animal subjects were used in the study.
Figures
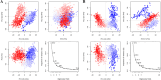
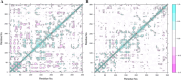
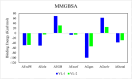
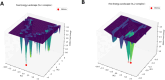
References
-
- Ahmad F, Gupta A, Marzook H et al (2024) Natural compound screening predicts novel GSK-3 isoform-specific inhibitors. Biochimie 225:68–80. 10.1016/j.biochi.2024.05.002 - PubMed
-
- Ajala A, Eltayb WA, Abatyough TM et al (2024a) In-silico screening and ADMET evaluation of therapeutic MAO-B inhibitors against Parkinson disease. Intell Pharm 2:554–564. 10.1016/j.ipha.2023.12.008
-
- Ajala A, Uzairu A, Shallangwa GA et al (2024b) QSAR application of natural therapeutics inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease through in-silico virtual-screening, docking-simulation, molecular dynamics, and pharmacokinetic prediction analysis. Intell Pharm 2:505–515. 10.1016/j.ipha.2023.12.004
-
- Alzforum (2019) Therapeutics: Tideglusib
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

