A CSF-1R inhibitor both prevents and treats triple-negative breast cancer brain metastases in hematogenous preclinical models
- PMID: 40760255
- PMCID: PMC12321670
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-025-10366-x
A CSF-1R inhibitor both prevents and treats triple-negative breast cancer brain metastases in hematogenous preclinical models
Abstract
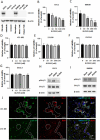
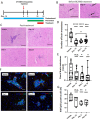
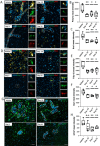
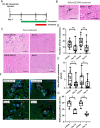
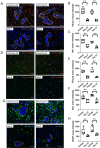
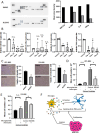
Brain metastasis is a common and serious complication of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) with few effective treatments. Here, we evaluated the effect of targeting the brain tumor microenvironment via the myeloid colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) pathway using the small molecule inhibitor BLZ945. Studies were conducted in two TNBC hematogenous brain-tropic models, 4T1-BR5 and 231-BR, with endpoints of prevention of brain metastasis formation and treatment of established brain metastasis. BLZ945 reduced the formation of brain metastases in both models by 57–65% (all p < 0.01) in the prevention setting. In the treatment setting, more analogous to the clinical situation, BLZ945 reduced the number and size of metastases in both models by 44–65% and 61–72%, respectively (all p < 0.05). Treatment with BLZ945 significantly reduced the number of myeloid cells in both the uninvolved brain and metastatic regions, by 15–54% across models as early as three days post-treatment. Efficacy was achieved without the need for complete suppression of brain myeloid cells, suggesting that potential adverse effects of full myeloid suppression can be minimized. Additionally, BLZ945 reduced cancer cell proliferation and astrocyte activation in the tumor microenvironment in vivo. In vitro studies showed that BLZ945 inhibited the secretion of inflammatory cytokines that stimulated cancer cell invasion; BLZ945 also indirectly reduced cancer cell proliferation through astrocyte interaction. Our findings suggest that microglial CSF-1R controls a series of myeloid regulatory pathways, both alone and in concert with other brain microenvironmental cells. The data preclinically credential CSF-1R inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy for TNBC brain metastases.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s10585-025-10366-x.
Keywords: Astrocyte; BLZ945; Brain metastasis; Colony-stimulating factor-1; Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor; Macrophage; Microglia; Triple-negative breast cancer; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BLZ945 derivatives for PET imaging of colony stimulating factor-1 receptors in the brain.Nucl Med Biol. 2021 Sep-Oct;100-101:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Nucl Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34174546
-
Aging and CNS Myeloid Cell Depletion Attenuate Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 1;27(15):4422-4434. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1549. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34083229 Free PMC article.
-
Colony Stimulating Factor-1 (CSF-1) and Interleukin-34 (IL-34) Differentially Alter White Matter and Gray Matter Microglia and Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells.J Neurochem. 2025 Aug;169(8):e70186. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70186. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40741719
-
Colony Stimulating Factor-1 Receptor: An emerging target for neuroinflammation PET imaging and AD therapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Feb 15;100:117628. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117628. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38330850 Review.
-
Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling in the central nervous system and the potential of its pharmacological inhibitors to halt the progression of neurological disorders.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Jun;30(3):821-842. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00958-4. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35290551 Review.
References
-
- Morris PG et al (2012) Limited overall survival in patients with brain metastases from triple negative breast cancer. Breast J 18(4):345–350 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

