Predictive value of immune inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index for contrast-induced acute kidney injury in endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 40760557
- PMCID: PMC12323997
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043642
Predictive value of immune inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index for contrast-induced acute kidney injury in endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
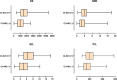
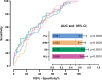
Endovascular treatment (EVT) is the treatment method for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) caused by large vessel occlusion. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) is a relatively common complication. In this study, we aimed to investigate the incidence and possible risk factors of CI-AKI including systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy. We retrospectively analyzed patients who underwent EVT for acute cerebral large vessel occlusion between January 1, 2021, and March 31, 2024. Before the intervention, blood was drawn from the antecubital vein and collected in the appropriate tubes. Serum levels of neutrophils, lymphocytes, platelets, hemoglobin, CRP, and albumin were measured, alongside lipid profiles and liver and kidney function parameters. An increase in serum creatinine of 0.5 mg/dL or more than 25% in the measurements 48 to 72 hours after EVT compared to before was defined as CI-AKI. SII was calculated with the formula of: peripheral (platelet count × neutrophil count)/ lymphocyte count; SIRI was calculated with the formula of: (neutrophil count × monocyte count)/ lymphocyte count. Their predictive value for CI-AKI occurrence was compared. CI-AKI was detected in 54 (19%) of the 281 patients included in the study. In terms of clinical parameters, baseline NIHSS, postthrombectomy, cerebral edema, hemorrhagic transformation, recanalization time, discharge mRS and contrast amount were significantly higher in patients with CI-AKI. SII exhibited the highest discriminative performance in predicting CI-AKI in patients undergoing mechanical thrombectomy, with a threshold of > 1784 (AUC = 0.710, 95% CI: 0.631-0.788, P < .001, sensitivity 42.6%, specificity 89.0%) followed by SIRI (AUC = 0.652, 95% CI: 0.576-0.728, P < .001, sensitivity 88.9%, specificity 37.9%). SII and SIRI were found to be significantly higher in patients with CI-AKI. These scores may be new promising low-grade inflammatory indicators for predicting CI-AKI development.
Keywords: contrast-induced acute kidney injury; endovascular treatment; systemic immune inflammation index; systemic inflammation response index.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive value of systemic inflammatory indices for perinatal outcomes following cervical cerclage: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 10;25(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07888-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40640782 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective observational study on the prognostic role of inflammatory markers in futile recanalization after endovascular treatment for large-vessel stroke.J Int Med Res. 2025 Jul;53(7):3000605251359474. doi: 10.1177/03000605251359474. Epub 2025 Jul 30. J Int Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40736149 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index as a predictor of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in coronary artery disease: a multicenter cohort study.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2474204. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2474204. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40125941 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular thrombectomy with versus without intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 24;4(4):CD015721. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015721.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40271574
-
Endovascular Thrombectomy for Carotid Pseudo-Occlusion in the Setting of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Comparative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Sep 9;45(9):1241-1245. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8268. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38575320
References
-
- Oliveira M, Rocha A, Barbosa F, et al. Acute kidney injury after endovascular therapy in acute stroke patients: systematic review with meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023;15:e468–74. - PubMed
-
- Weber R, van Hal R, Stracke P, Hadisurya J, Nordmeyer H, Chapot R. Incidence of acute kidney injury after computed tomography angiography ± computed tomography perfusion followed by thrombectomy in patients with stroke using a postprocedural hydration protocol. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9:e014418. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alqahtani F, Osman M, Harris AH, Hohmann SF, Alkhouli M. Mortality and functional outcomes of endovascular stroke therapy in the United States. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2021;97:470–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

