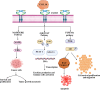
Dual role of CXCL10 in cancer progression: implications for immunotherapy and targeted treatment
- PMID: 40760734
- PMCID: PMC12326575
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2538962
Dual role of CXCL10 in cancer progression: implications for immunotherapy and targeted treatment
Abstract
CXCL10 is a chemokine crucial for immune cell recruitment and inflammation modulation, especially within the tumor microenvironment. This review critically analyzes the underexplored role of CXCL10 in modulating JAK/STAT, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt pathways across different tumor types, highlighting inconsistencies in current research and proposing novel therapeutic strategies based on research from databases such as PubMed and Scopus. Future targeted therapies could include personalized approaches that either enhance the immunostimulatory functions of CXCL10 or inhibit its tumor promoting effects. Techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of CXCL10 has demonstrated potential in preclinical models to reduce tumor-promoting inflammation, while nanoparticle-based CXCL10 inhibitors enhance immune checkpoint blockade efficacy in melanoma. In addition, targeting CXCL10-related mechanisms of immune evasion such as inhibition of CXCR3 may help to prevent metastasis. Futureresearch should focus on CXCL10-targeting approaches in highly immunosuppressive tumors, such as pancreatic and glioblastoma, where immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown limited efficacy.
Keywords: CXCL10; immune regulation; signaling pathway; therapeutic strategies; tumor immune evasion ; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ, Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML, Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, et al. Sustained proliferation in cancer: mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S25–20. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous