Flow diverter stent for the treatment of ruptured distal anterior cerebral artery: A retrospective multicenter analysis from CRETA registry
- PMID: 40760906
- PMCID: PMC12325231
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199251348514
Flow diverter stent for the treatment of ruptured distal anterior cerebral artery: A retrospective multicenter analysis from CRETA registry
Abstract
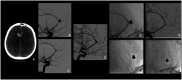
BackgroundData on off-label use of flow diverter for ruptured distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms (rDACAAs) are limited. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of flow diversion for rDACAAs in a large multicenter cohort.MethodsA retrospective observational study on consecutive patients who were treated with flow diversion for rDACAAs at 8 centers in 4 countries was performed. Primary outcome was the occlusion rate of the target aneurysm at the last radiological follow-up. Secondary outcomes included good clinical outcome, retreatment, technical success, procedure-related complications, radiological outcome of the covered branches and mortality rate.ResultsA total of 21 patients with 21 rDACAAs were treated between January 2017 and December 2024. Thirteen patients were women (61.9%) and the median age was 54 years (IQR 46-66). The most common etiology was saccular (71.4%), followed by dissecting (23.8%) and mycotic (4.8%). In all patients a single stent was successful deployed. Median imaging follow-up was 9 (7-12) months. At last follow-up adequate occlusion was 95.2%. Symptomatic thromboembolic or hemorrhagic complications occurred in 9.5% of patients. Seventeen patients (81%) had good clinical outcome (mRS 0-2) with mortality rate of 9.5%. In-stent stenosis occurred in one case that was conservatively managed without major concerns.ConclusionsFlow diversion is feasible as a potential treatment strategy for acutely ruptured aneurysms arising from distal anterior cerebral artery. Flow diverter may represent a valid option whenever other treatments are considered challenging or high risk.
Keywords: Ruptured aneurysm; distal anterior cerebral aneurysm; flow diverter stent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Kühn AL, Gounis MJ, Puri AS. Introduction: history and development of flow diverter technology and evolution. Neurosurgery 2020; 86: S3–S10. - PubMed
-
- Patel PD, Chalouhi N, Atallah E, et al. Off-label uses of the pipeline embolization device: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 2017; 42: E4. - PubMed
-
- Griessenauer CJ, Ogilvy CS, Foreman PM, et al. Pipeline embolization device for small intracranial aneurysms: evaluation of safety and efficacy in a multicenter cohort. Neurosurgery 2017; 80: 579–5878. - PubMed
-
- Fischer S, Perez MA, Kurre W, et al. Pipeline embolization device for the treatment of intra and extracranial fusiform and dissecting aneurysms: initial experience and long-term follow-up. Neurosurgery 2014; 75: 364–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

