Gastric banding adjustment catheter dislodgement and perforation into the colon: case report
- PMID: 40761195
- PMCID: PMC12319585
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-24-240
Gastric banding adjustment catheter dislodgement and perforation into the colon: case report
Abstract
Background: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is a safe and effective method in bariatric surgery. Complications, which are relatively rare (10-20%), are related either to the band such as band slippage, pouch dilation, band erosion, intraluminal band migration or to the port-adjustment-tube system such as infection, tube disconnection and dislocation. Dislocation of the adjustment catheter perforating into the colon is extremely rare, our present case is the third publication on this complication.
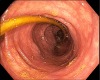
Case description: In our present case, we report on an asymptomatic patient with intraluminal penetration of the dislodged adjustment tube into the colon 26 years after implantation of a gastric banding system. We revealed the complication randomly by positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) in the course of a tumor staging of a newly diagnosed lung cancer. The gastric band was removed laparoscopically, the adjustment tube however, had to be cut through due to extended adhesions and could only partially be removed. The rest of the catheter passed spontaneously via rectum on the following day.
Conclusions: Intraluminal penetration of the dislodged adjustment tube into the colon is extremely rare and may be asymptomatic such as in case of our patient. Other relevant complications after gastric band implantation may also remain undetected. During long-term follow up, occasionally performed imaging should be considered also in asymptomatic patients with implanted gastric banding system.
Keywords: Morbid obesity; adjustment tube migration; case report; gastric banding; intracolonic penetration.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://acr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/acr-24-240/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Carbon dioxide detection for diagnosis of inadvertent respiratory tract placement of enterogastric tubes in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 19;2(2):CD011196. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011196.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39968844
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery for the treatment of obesity in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 8;9(9):CD011740. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011740.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36074911 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Stage Pedicle Preputial Tube Substitution Urethroplasty with Corpora Cavernosa Augmentation Using Buccal Mucosa Graft for Primary Peno-Scrotal Hypospadias Re-pair in Adults.Int Braz J Urol. 2025 Jul-Aug;51(4):e20240650. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2024.0650. Int Braz J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40105707 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
