Case report of long-term disease control of recurrent intraoral basal cell carcinoma with vismodegib at two-year follow-up
- PMID: 40761207
- PMCID: PMC12319617
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-24-235
Case report of long-term disease control of recurrent intraoral basal cell carcinoma with vismodegib at two-year follow-up
Abstract
Background: Intraoral basal cell carcinoma (IOBCC) is an extremely rare cancer and is usually treated with surgical excision. However, the management of recurrent IOBCC not amenable to resection is unknown. We report a case of effective treatment of recurrent IOBCC with vismodegib with rapid and durable response following only 6 months of treatment.
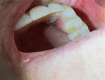
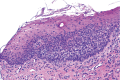
Case description: A 60-year-old female with IOBCC was first diagnosed in August 2016 involving right buccal mucosa and right anterior hard palate. She subsequently underwent wide local excision with involved margins. Her first local recurrence occurred four and a half years after initial diagnosis and went on to have further surgical resection. Her second local recurrence occurred 2 years later, where further surgery and radiotherapy were not amenable. She was then treated with vismodegib 150 mg daily, delivered via her gastrotomy feeding tube and she achieved clinical complete response within 3 months of treatment. Following 6 months of treatment, due to progressive side effects, she ceased treatment. She remains on surveillance and disease-free on clinical examination and repeat biopsy for the past 2 years. To our knowledge, this is the first case of inoperable recurrent IOBCC treated with vismodegib, delivered via gastrotomy tube, leading to a durable complete response. The patient's tumour showed significant regression within 3 months of treatment initiation, with continued improvement over the following year. The rapid and durable response to vismodegib in this case is particularly noteworthy, considering the aggressive nature of recurrent IOBCC and the patient's prior treatment history. The effective administration of vismodegib through a gastrostomy feeding tube is an additional important clinical finding. This approach demonstrates the flexibility of vismodegib treatment and may be applicable to other patients facing feeding or medication administration challenges.
Conclusions: Vismodegib can induce rapid, effective, and durable responses in IOBCC. The administration of vismodegib via gastrotomy tube was found to be safe and did not compromise its efficacy. Longer-term and larger cohort follow-up studies are needed to fully evaluate the efficacy and safety of vismodegib in this patient population.
Keywords: Intraoral basal cell carcinoma (IOBCC); case report; vismodegib.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://acr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/acr-24-235/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
