A multimodal nomogram for benign-malignant discrimination of lung-RADS ≥4A nodules: integration of oxygen enhanced zero echo time MRI, CT radiomics, and clinical factors
- PMID: 40761252
- PMCID: PMC12318770
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1563073
A multimodal nomogram for benign-malignant discrimination of lung-RADS ≥4A nodules: integration of oxygen enhanced zero echo time MRI, CT radiomics, and clinical factors
Abstract
Background and objective: Lung-RADS ≥4A nodules require urgent intervention. Low-dose CT (LDCT), the primary screening tool, involves cumulative radiation exposure-critical for patients with serial scans. Oxygen-enhanced zero-echo time MRI (OE-ZTE-MRI) shows potential for lung nodule evaluation. However, its additive value when combined with CT radiomics and clinical factors for Lung-RADS ≥4A nodules remains unproven. This study aimed to develop a preoperative prediction model integrating OE-ZTE-MRI/CT radiomics and clinical factors for benign-malignant discrimination of Lung-RADS ≥4A nodules and compare its performance against single-modality models.
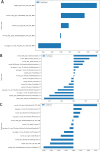
Methods: 99 nodules from 84 prospectively enrolled patients undergoing both LDCT and OE-ZTE-MRI were included. Nodule boundaries were manually contoured as regions of interest (ROIs) on both modalities. Six machine learning classifiers were applied to radiomic features (extracted from LDCT and OE-ZTE-MRI) and clinical parameters (age, smoking history, nodule diameter, calcification, etc.). Model performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves with area under the curve (AUC), complemented by decision curve analysis (DCA). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression identified independent predictors, which were incorporated into a final nomogram to visualize clinical-radiomic prediction.
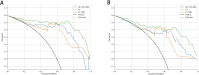
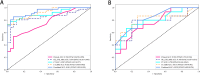
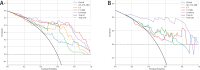
Results: MRI model had a similar diagnostic performance to CT model (MRI vs. CT: training cohort AUC: 0.854 vs 0.907; testing cohort AUC: 0.769 vs 0.798). Multi-radiomics model achieved the highest diagnostic efficiency (train cohort AUC:0.923; testing cohort AUC: 0.813). Multivariate Logistic regression showed that nodule diameter (p=0.005) and calcification (p=0.029) were important factors affecting the benign and malignant nodules. The nomogram constructed by 3 models(CT/OE-ZTE-MRI/Clinical factors) achieved the best preoperative prediction performance for benign and malignant nodules (training cohort: AUC 0.941; testing cohort AUC:0.838).
Conclusion: The nomogram combining OE-ZTE-MRI/CT radiomics and clinical factors (nodule diameter, calcification) improves preoperative discrimination of Lung-RADS ≥4A nodules (AUC=0.838), outperforming single-modality models. This tool enables evidence-based triage, potentially reducing unnecessary invasive procedures.
Keywords: CT; MRI; multimodel analysis; oxygen enhanced; radiomics.
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Liu, Li, Qin, Guan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Iaccarino JM, Simmons J, Gould MK, Slatore CG, Woloshin S, Schwartz LM, et al. Clinical equipoise and shared decision-making in pulmonary nodule management. A survey of american thoracic society clinicians. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2017) 14:968–75. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201609-727OC, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

