Reirradiation with stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas - a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40761290
- PMCID: PMC12320082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2025.100989
Reirradiation with stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas - a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a widely used treatment modality for vestibular schwannomas due to its non-invasive nature and high tumor control rates. However, some patients experience tumor progression after treatment. In this setting, reirradiation with SRS represents a potential treatment option. This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the evidence for reirradiation of vestibular schwannomas with SRS.
Methods: This systematic literature review and meta-analysis investigates the efficacy and safety of reirradiation with SRS for vestibular schwannoma and was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA).
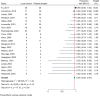
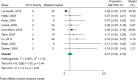
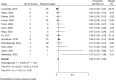
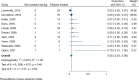
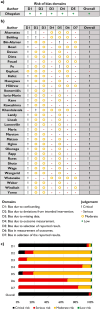
Results: A total of 806 studies were screened and 35 included, comprising 394 reirradiated patients. The median time from first treatment to reirradiation was 45 months (range: 12 - 65 months). Reirradiation with SRS, applying a median marginal/prescription dose of 12 Gy, achieved an estimated local control of 95% (95% confidence interval (CI): 92 - 97%, I2 = 29.62%, p = 0.10). Trigeminal and facial nerve deterioration rates after repeat SRS were 7% (95% CI: 4 - 10%, I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.44) and 6% (95% CI: 3 - 8%, I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.53), respectively. Serviceable hearing after reirradiation with SRS was rare (5%, 95% CI: 2 - 8%, I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.46). Among patients with serviceable hearing before reirradiation, 43% maintained it after treatment (95% CI: 29 - 57%, I2 = 65.71%, p = 0.00). The risk of bias across all studies was high.
Conclusion: Reirradiation with SRS appears to be a safe and effective salvage treatment for progressive vestibular schwannomas. Prospective studies are warranted to define the optimal dose, timing, and dose constraints for reirradiation.
Keywords: Acoustic neuroma; Radiosurgery; Reirradiation; Stereotactic radiosurgery; Vestibular schwannoma.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Felix Ehret has received honoraria and travel support from ZAP Surgical Systems, Inc., and Accuray, Inc., and acknowledges research funding from the German Cancer Aid and Accuray, Inc., all unrelated to the submitted work. The other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

