Hydrogels and nanogels: effectiveness in dermal applications
- PMID: 40761321
- PMCID: PMC12320743
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.16.90
Hydrogels and nanogels: effectiveness in dermal applications
Abstract
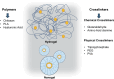
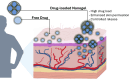
Drug delivery systems (DDSs) are an important tool for obtaining medicines with improved physicochemical properties, especially for drugs with stability, absorption, and biodistribution impairments. Among the DDSs, we can highlight hydrogels and nanogels, which are easy to obtain, show good biocompatibility, and have several applications in the design of drug carriers for dermal and ocular administration. In this review, we introduce a brief concept on hydrogels, underlining compounds such as chitosan and alginate, and methods used for their preparation. Nanogels, with their attractive features, such as high drug encapsulation and penetration enhancer embedding, are also addressed. Finally, the application of these systems in dermal pathophysiological processes through the incorporation of drugs for enhancing skin permeation brings out promising prospects for innovation which may arise in the drug delivery field.
Keywords: cross-linking; drug delivery; formulation; nanogel; polymer.
Copyright © 2025, Ludwig et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
References
-
- Rosiak J M, Yoshii F. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect B. 1999;151:56–64. doi: 10.1016/s0168-583x(99)00118-4. - DOI
-
- Baker W O. Rubber Chem Technol. 1949;22:935–955. doi: 10.5254/1.3543023. - DOI
-
- Simaljakova J. Cesko-Slov Farm. 1955;4:11–14. - PubMed
-
- Buri P, Gumma A, Mirianoff A. Pharm Acta Helv. 1966;41:480–485. - PubMed
-
- Scherenzel M. Pharm Acta Helv. 1964;39:546–555. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
