Comparing the effects of 25-minute electrical muscle stimulation vs. 90-minute full-body resistance training on body composition and strength: A 20-week intervention
- PMID: 40761504
- PMCID: PMC12320652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2025.07.002
Comparing the effects of 25-minute electrical muscle stimulation vs. 90-minute full-body resistance training on body composition and strength: A 20-week intervention
Abstract
Objectives: Electromyostimulation (EMS) and traditional resistance training (TradRT) are widely used methods for improving muscle strength and body composition. However, comparative studies employing a multi-week longitudinal design remain limited. This study aimed to investigate the effects of 20 weeks of EMS vs. TradRT on body composition and strength performance in physically active adults.
Methods: Forty-six participants were randomly assigned to either the EMS group (n = 22) or the TradRT group (n = 24). The EMS group performed twice-weekly, 25-min whole-body EMS sessions, while the TradRT group completed twice-weekly, 90-min full-body resistance training sessions.
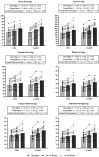
Results: Assessments of body weight, body mass index (BMI), fat percentage, and maximal strength were conducted at baseline, 10 weeks, and 20 weeks. A significant time effect was observed for all variables (p < 0.001), indicating improvements in both groups. However, group × time interactions revealed distinct adaptation patterns. The TradRT group exhibited greater reductions in body fat percentage and superior strength gains in bench press, leg press, shoulder press, and triceps pushdown, and abdominal strength. Conversely, the EMS group showed greater reductions in body weight and BMI. No significant interaction effect was observed for biceps curl strength. Both EMS and TradRT were effective in improving strength and body composition, but TradRT led to greater strength development and fat reduction, while EMS was more effective for weight and BMI reduction.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that EMS may serve as a viable alternative for individuals unable to engage in high-load resistance training, whereas TradRT remains superior for maximizing strength and fat loss.
Keywords: Body composition; EMS; Electromyostimulation; Muscle strength; Resistance training; Strength adaptation.
© 2025 The Society of Chinese Scholars on Exercise Physiology and Fitness. Published by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Apr 30;(4):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3:CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. PMID: 23633361 Updated.
-
Effect of Resistance Training Frequency on Gains in Muscular Strength: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2018 May;48(5):1207-1220. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0872-x. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29470825
-
Dose-Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1693-720. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0385-9. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26420238 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources