Engineering DNA nanopores: from structural evolution to sensing and transport
- PMID: 40761509
- PMCID: PMC12320668
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102137
Engineering DNA nanopores: from structural evolution to sensing and transport
Abstract
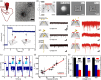
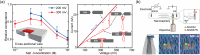
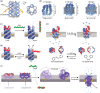
Synthetic nanopores, inspired by natural ion channels and nuclear pore complexes, hold immense potential for elucidating cellular transport mechanisms and enhancing molecular sensing technologies. DNA nanotechnology, particularly DNA origami, stands out as a transformative platform for designing biomimetic nanopores, leveraging its biocompatibility, structural programmability, and mechanical tunability. This review traces the structural evolution of DNA nanopores across three phases: early hybrid designs with solid-state platforms, vertically-inserted nanopores in lipid bilayers, and horizontally-arranged nanopores with advanced functionalities. Unlike prior reviews, we integrate this progression with critical insights into limitations-such as stability, scalability, and noise-while highlighting breakthroughs in single-molecule sensing and controlled transmembrane transport. We conclude by outlining strategies for next-generation DNA nanopores, offering a roadmap for their optimization in synthetic biology and nanomedicine.
Keywords: DNA origami; Molecular sensing; Nanopores; Transmembrane transport.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- He Y., Tsutsui M., Zhou Y., Miao X.-S. Solid-state nanopore systems: from materials to applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2021;13:48. doi: 10.1038/s41427-021-00313-z. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

