Polydopamine@Zinc oxide coated macroporous membrane for antibacterial protection and early pulp repair in pulpitis
- PMID: 40761514
- PMCID: PMC12320747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102109
Polydopamine@Zinc oxide coated macroporous membrane for antibacterial protection and early pulp repair in pulpitis
Abstract
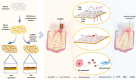
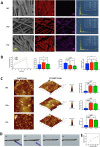
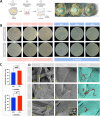
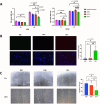
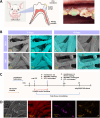
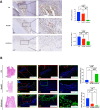
Continuous decompression and drainage are a vital surgical strategy for managing severe tissue infections. In vital pulp therapy (VPT) for irreversible pulpitis, there is a clinical demand for advanced biomaterials capable of effectively sealing the pulp cavity, alleviating pulpal hypertension, preventing bacterial infiltration, and resolving acute pulp inflammation in bacteria-rich environments. In this study, we developed a polydopamine@zinc oxide nanoparticle (ZnO-NP)-coated polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane with tunable Zn content ranging from 2.51 to 7.45 wt%. The polydopamine enhanced ZnO-NP adhesion to the PTFE membrane, enabling superior fluid permeability and robust antibacterial efficacy against E. faecalis and S. mutans, while maintaining excellent biocompatibility. In a minipig pulpitis model, the ZnO-coated membrane significantly outperformed iRootBP PLUS by promoting faster dentine bridge formation (934.0 ± 91.3 μm vs. 116.3 ± 45.4 μm), preserving the integrity of the underlying pulp tissue and inducing M2 macrophage polarization.These findings deomstrate that ZnO-functionalized fibrous membrane can address key challenges in VPT by alleviating pulp hypertension, preventing microbial invasion, and simultaneously promoting pulp tissue regeneration. This approach offers a promising strategy to enhance tharepeutic outcomes of vital pulp therapy.
Keywords: Antimicrobial effect; Irreversible pulpitis; Polydopamine; Vital pulp therapy; ZnO-Coated biomaterial.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Management strategies for pulpitis in vital permanent teeth in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2025 Jun;26(3):451-463. doi: 10.1007/s40368-025-01021-w. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2025. PMID: 40117109
-
Vital Pulp Therapy in Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses.Pediatr Dent. 2025 May 15;47(3):137-150. Pediatr Dent. 2025. PMID: 40533920
-
Revolutionizing the diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis - Current strategies and future directions.J Oral Biosci. 2024 Jun;66(2):272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2024.03.006. Epub 2024 Mar 18. J Oral Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38508491 Review.
-
Vital pulp therapy-Factors influencing decision-making for permanent mature teeth with irreversible pulpitis: A systematic review.Int Endod J. 2024 May;57(5):505-519. doi: 10.1111/iej.14036. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Int Endod J. 2024. PMID: 38326290
-
Emerging trends of injectable hydrogels for vital pulp therapy: A comprehensive review.Int Endod J. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1111/iej.14279. Online ahead of print. Int Endod J. 2025. PMID: 40650334 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

