Targeting immune checkpoints as a new therapeutic strategy for intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 40761520
- PMCID: PMC12319215
- DOI: 10.34172/bi.31086
Targeting immune checkpoints as a new therapeutic strategy for intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
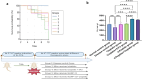
Introduction: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (IH-CCA) is a malignancy characterized with limited response to standard chemotherapeutic strategies due to development of drug resistance. We aim to investigate new immune-therapeutic strategy through using AUNP-12 as an immune checkpoint blocker in chemically induced IH-CCA mice model.
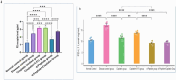
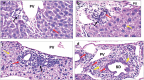
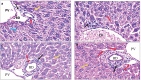
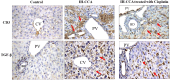
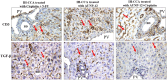
Methods: Mice were randomly divided into 2 groups; normal control group and disease group. The disease group was further subdivided into 5 subgroups assigned according to treatment modality. The Immunotherapeutic mechanism of AUNP-12 was investigated through analysis of PD-1/PD-L1 levels and IFN-γ Levels in the tumor microenvironment. Immunohistochemical analysis of CD3+T lymphocytes and TGF-β was performed.
Results: We reported that AUNP-12 significantly decreased levels of PD-1/PD-L1 at the site of tumor with subsequent activation of CD3+T lymphocytes that secrete IFN-γ which specifically lysis tumor cells. AUNP-12 also acts through downregulation of TGF-β signaling in IH-CCA mice group treated with AUNP-12.
Conclusion: Our data indicated that AUNP-12 effectively harbors IH-CCA progression and improves the survival rate of mice. AUNP-12 acts as an immune check point blocker that specifically inhibits PD-1/PD-L1 binding, activates cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and downregulates TGF-β signaling pathway.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Immune checkpoint blockade; Intra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma; PD-1/PD-L1; d-Peptide.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials