New insights in fluid monitoring for surgical patients. A concept study
- PMID: 40761610
- PMCID: PMC12318955
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2025.1619238
New insights in fluid monitoring for surgical patients. A concept study
Abstract
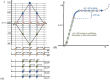
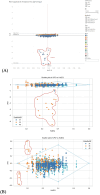
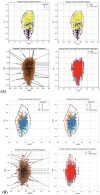
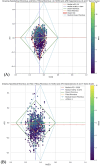
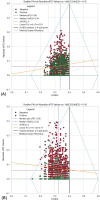
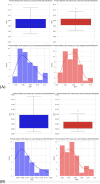
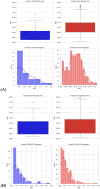
Purpose: This study evaluates the primary hypothesis of red cell mass (RCM) dependent amplitude of homeostatically acceptable limits of fluctuation in plasma dilution by exploring the correlation between RCM-specific equilibrated hematocrit (EQ_Hct) and amplitude of plasma dilution during perioperative mini Volume Loading Test (mVLT).
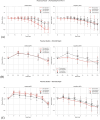
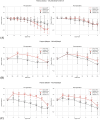
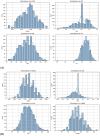
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from our previous RCTs, including 1,651 invasive arterial plasma dilution (aPD), 1,645 noninvasive "capillary" plasma dilution (cPD) and 236 estimates of EQ_Hct from 236 perioperative mVLT sessions. The cPD was estimated using noninvasive hemoglobin (SpHb, Masimo Radical 7, Irvine, CA) measurement. Fixed number of crystalloid boluses was used in 36 and 48 elective total knee arthroplasty (TKA) patients, and individualized number of boluses in 34 total hip arthroplasty (THA) patients for whom the number of boluses depended on the advices by our prototype automated clinical decision support system (ACDSS).
Results: The primary hypothesis was confirmed-aPD decreased as EQ_Hct decreased when EQ_Hct <40%, and a very weak positive correlation was found between EQ_Hct and absolute aPD (Spearman's correlation coefficient 0.1025, p < 0.001). It was also confirmed when non-invasive data sets were used. A very weak negative correlation between HctEQ values and absolute cPD values (Spearman's correlation coefficient 0.0640, p = 0.0149).
Conclusion: This study points to the feasibility of Photoplethysmography (PPG) based estimates of hemoglobin concentration for continuous noninvasive monitoring of fluid accumulation and detecting imminent edema using the Homeostatic Blood States (HBS) theory and transcapillary reflux model. The ACDSS-guided fluid loading has a potential to minimise unnecessary fluid accumulation. Further research is needed to explore and improve these techniques.
Keywords: hematocrit; hemodilution; hemoglobin; hydration; innovative technique; perioperative fluid therapy; plasma dilution; transcapillary reflux.
© 2025 Andrijauskas, Andrijauskas, Dilijonas, Jovaiša, Marozas, Stankevičius, Kerroum, Čincikas, Švedienė, Kvederas, Porvaneckas and Svensen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Hahn RG. Clinical Fluid Therapy in the Perioperative Setting. 2 ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; (2016).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

