Clinical and Genetic Profile of Pediatric and Adult Wilson's Disease in India
- PMID: 40761701
- PMCID: PMC12320151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100717
Clinical and Genetic Profile of Pediatric and Adult Wilson's Disease in India
Abstract
Background and aims: Wilson's disease (WD) is a disorder of copper metabolism caused by a mutation in the ATP7B gene. We aimed to comprehensively evaluate the clinical and genetic profiles of patients with WD.
Methods: This was a single-center retrospective study conducted at AIG Hospitals, Hyderabad, India. Patients diagnosed and treated for WD both in outpatient and inpatient settings from June 2020 to April 2024 were included.
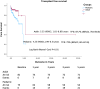
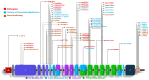
Results: A total of 156 patients (women being 33.3%) with a median age of 19 years (2-57) were included from June 2020 to April 2024. Forty eight percent (n = 75) patients were of pediatric age <19 years. Clinical presentation with liver disease in the pediatric population included 26.7% with acute liver failure and 20% as acute-on-chronic liver failure compared to 30.9% with decompensated cirrhosis in the adults. On Kaplan-Meier analysis, in the pediatric group, the transplant-free survival was 72% (95% confidence interval [CI], 60.4-81.8) compared to 87.7% (95% CI, 78.5-93.9) in the adult group (P = .01) after a median duration of follow-up of 1.33 years (range, 0.01-24). Thirteen percent of patients underwent living donor liver transplantation, 0.7% (n = 1) patients developed cholangiocarcinoma, and 0.7% (n = 1) underwent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Seventy percent of patients underwent genetic evaluation for ATP7B mutations and 54.1% (59 of 109) were homozygous or compound heterozygous for a combination of either pathogenic variant and/or variants of uncertain significance. The most common pathogenic ATP7B variants were p.Gly977Glu, p.Cys271Ter, and p.Asn1186Ser.
Conclusion: Pediatric patients with WD present more often with an acute illness and have lower transplant-free survival compared to adults, with ATP7B mutations identified in over half of those tested, highlighting the need for early genetic evaluation and tailored management.
Keywords: ATP7B Gene; Acute Liver Failure; Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure; Cirrhosis; Leipzig Score; Liver Transplantation.
© 2025 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Yamaguchi H., Nagase H., Tokumoto S., et al. Prevalence of Wilson disease based on genome databases in Japan. Pediatr Int. 2021;63:918–922. - PubMed
-
- Devarbhavi H., Singh R., Adarsh C.K., et al. Factors that predict mortality in children with Wilson disease associated acute liver failure and comparison of Wilson disease specific prognostic indices. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:380–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

