Obtaining higher yield and quality rapeseed protein: complex enzymatic hydrolysis assisted alkaline water extraction of cold pressed-extracted rapeseed meal
- PMID: 40761753
- PMCID: PMC12320185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102837
Obtaining higher yield and quality rapeseed protein: complex enzymatic hydrolysis assisted alkaline water extraction of cold pressed-extracted rapeseed meal
Abstract
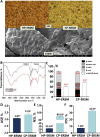
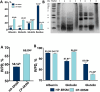
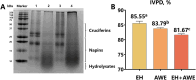
In this experiment, rapeseed meal (RSM) was subjected to different pressing temperatures (75 °C and 150 °C) and extraction method (enzymatic hydrolysis (EH), alkaline water extraction (AWE), and EH + AWE) were chosen to assess the effects of temperature on nutritional components, protein solubility (PS), secondary structure, fractions, and molecular weight (PMW), and in vitro protein digestibility (IVPD) of RSM and various methods on the extraction rate (ER), yield, and the characteristics of rapeseed protein (RP). The results indicated that high temperature caused some proteins to remain bound within the fiber, reduced PS and α-helix content, thereby complicating the extraction process. The RP extracted using EH + AWE showed higher ER, yield, PS, small PMW, and soluble sugar, lower glucosinolate content. This study established that EH + AWE of cold pressed-extracted RSM is a suitable method for RP extraction, providing a reference for the efficient development of RSM and the application of RP in the food industry.
Keywords: Alkaline water extraction; Enzymatic hydrolysis; Enzymatic hydrolysis assisted alkaline water extraction; Rapeseed meal; Rapeseed protein; Temperature.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantifying protein digestion kinetics of feed ingredients using a modified in vitro incubation assay.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf190. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf190. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40577075 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of yeast-enriched functionalized canola meal supplementation on apparent total tract macronutrient digestibility and fecal characteristics, fecal microbiota, and immune function of healthy adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae224. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae224. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39101402 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent Digestibility Coefficients of Selected Plant Protein Feed Ingredients and Feeds for Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) Postsmolts Cultured in Fresh Water.Aquac Nutr. 2025 Jul 28;2025:3047597. doi: 10.1155/anu/3047597. eCollection 2025. Aquac Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40761391 Free PMC article.
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Heated insufflation with or without humidification for laparoscopic abdominal surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 19;10(10):CD007821. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007821.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27760282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aider M., Barbana C. Canola proteins: Composition, extraction, functional properties, bioactivity, applications as a food ingredient and allergenicity – A practical and critical review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2011;22(1):21–39. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2010.11.002. - DOI
-
- Anderson-Hafermann J.C., Zhang Y., Parsons C.M. Effects of processing on the nutritional quality of canola meal. Poultry Science. 1993;72(2):326–333. doi: 10.3382/ps.0720326. - DOI
-
- Araba M., Dale N.M. Evaluation of protein solubility as an indicator of overprocessing soybean meal. Poultry Science. 1990;69(1):76–83. doi: 10.3382/ps.0690076. - DOI
-
- Bagnani M., Ehrengruber S., Soon W.L., Peydayesh M., Miserez A., Mezzenga R. Rapeseed cake valorization into bioplastics based on protein amyloid fibrils. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2023;8(3):2200932. doi: 10.1002/admt.202200932. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

