Digital assistive technologies for community-dwelling people with dementia: A systematic review of systematic reviews by the INTERDEM AI & assistive technology taskforce
- PMID: 40761778
- PMCID: PMC12319280
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076251362353
Digital assistive technologies for community-dwelling people with dementia: A systematic review of systematic reviews by the INTERDEM AI & assistive technology taskforce
Abstract
Introduction: The use of digital assistive technologies by and for people living with dementia is promising for supporting social health and advocated as a partial solution to growing prevalence worldwide. A state-of-the-art position paper published in 2017 identified challenges regarding digital assistive technologies, around five themes: development, usability, (cost-)effectiveness, implementation and ethics. This systematic review summarizes progress on the challenges found in 2017, and persisting or emerging challenges.
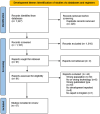
Methods: A systematic review of systematic reviews was conducted, focused on studies published after 2016. The inclusion criteria required that the target group included, at least in part, people with dementia living in the community and that the technologies aimed to support social health. For the five themes, literature searches were conducted in Medline, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Embase databases.
Results: A total of 112 reviews were included, covering various applications such as smart homes, care robots, exergaming and everyday technologies. No applications of artificial intelligence were included. The challenges included personalization of applications (development); limited use of standardized methods (usability); insufficient quantity and quality of randomized controlled trials (cost-effectiveness); overly high expectations of assistive technologies (implementation); and the need for more equitable access to technologies (ethics).
Conclusion: Much research has been conducted since the 2017 state of the art position paper. While some challenges identified at that time remain relevant, others have been addressed, and new challenges have emerged. Future research should prioritize emerging artificial intelligence applications; the development of integrated assistive technologies; evaluation using robust methods and meaningful outcomes; and the promotion of more accessible and inclusive technologies.
Keywords: Dementia; artificial intelligence; assistive technology; cost-effectiveness; development; digital health; ethics; implementation; systematic review; usability.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2023; 19: 1598–1695. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen HV, Mital S, Knopman DS, et al. Cost-effectiveness of lecanemab for individuals with early-stage Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2024; 102: e209218. - PubMed
-
- Amano T, Reynolds A, Scher C, et al. The effect of receiving a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias on social relationships of older adults. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2021; 50: 401–406. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources