Worldwide hotspots and trends in stem cell therapy for kidney disease in the last decade: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2015 to 2024
- PMID: 40761782
- PMCID: PMC12318756
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1619291
Worldwide hotspots and trends in stem cell therapy for kidney disease in the last decade: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2015 to 2024
Abstract
Background: Kidney disease represents a significant global health concern. Stem cell therapy has gained attention as a potential solution for chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, and end-stage renal disease. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the status of stem cell therapy for kidney disease through a systematic review of the literature.
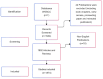
Methods: The literature included in this study was exclusively sourced from the Web of Science Core Collection. CiteSpace, VOSviewer, R-Bibliometrix, and the Literature Data Governance and Analysis System to evaluate factors such as publication quantity, author contributions, institutional involvement, geographic distribution, and keyword usage.
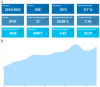
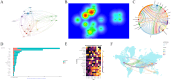
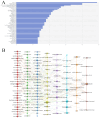
Results: This study on stem cell therapy for kidney disease included 1,874 articles. A significant number of publications came from China and the United States. The Mayo Clinic had the highest publication output, while Stem Cell Research & Therapy was the leading journal in terms of publication volume. Additionally, Lerman LO was the most prolific author in this field. Currently, there is a growing focus on mesenchymal stem cells and acute kidney injury models in this field. Future research is likely to explore topics such as extracellular vesicle-based therapies, various stem cell types, diabetic nephropathy, and membranous nephropathy.
Conclusion: This study applied bibliometric methods to assess the application and development of stem cell therapy for kidney disease over the past decade. It identified key research areas and forecasted future trends. The findings offer valuable insights for guiding future investigations into stem cell therapy for kidney disease.
Keywords: bibliometric; kidney disease; kidney injury; nephropathy; stem cell therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Liao, Zhang, Zhou, Wang, Chen, Ye, Zhou and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bibliometric and visual analysis of quercetin in kidney disease from 2000 to 2022.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 8;104(32):e43684. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043684. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40797391 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of research trends in mesenchymal stem cell therapy for neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia: 2004-2024.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 3;13:1558301. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1558301. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40530182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Comprehensive Global Analysis of Future Trends in Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Veterinary Medicine.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70258. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70258. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40145983 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge graph and bibliometric analysis of inflammatory indicators in ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;15:1533537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1533537. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40661780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

