Catalytic reduction/degradation of methyl orange by metal nanoparticle containing systems: a critical review
- PMID: 40761906
- PMCID: PMC12320226
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra04059k
Catalytic reduction/degradation of methyl orange by metal nanoparticle containing systems: a critical review
Abstract
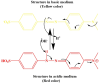
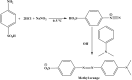
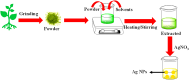
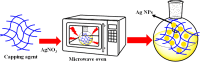
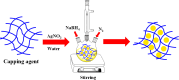
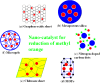
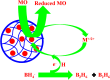
Organic dyes are widely used in many industries, producing health issues after being discharged into wastewater. Methyl orange (MO) is an organic azo dye which is also released into wastewater from different industries and causes toxicity in the environment. Recently, eco-friendly approaches to remove MO from water have garnered significant interest. Among these, the application of inorganic metal nanoparticles (IMNPs) for the catalytic and photocatalytic reduction of MO is an emerging approach for effective and sustainable pollutant remediation. Various IMNPs, which are used for reduction of MO or conversion of MO into eco-friendly products recently through catalytic and photocatalytic reactions, are discussed in this review, as is the synthesis of mono- and bimetallic nanoparticles with and without capping agents which affect their stabilization as well as catalytic performance against MO. The capping agents enhance the catalytic performance of both mono- and bimetallic nanoparticles, recyclable properties, and tuning ability. Additionally, the characterization techniques employed to examine the properties of IMNPs and to monitor the catalytic reduction of MO are discussed. Future research directions should prioritize the separation and characterization of the products formed after MO catalytic treatment to assess their potential applications and improve reaction rates.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
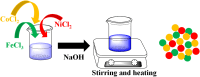

Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Functionalization of halloysite nanotubes as remediation agents for organic and inorganic contaminants: Insights into synthesis routes, removal techniques, and eco-friendly perspectives.Sci Total Environ. 2025 Aug 10;989:179771. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2025.179771. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Sci Total Environ. 2025. PMID: 40505512 Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
An evidence-based environmental perspective of manufactured silver nanoparticle in syntheses and applications: a systematic review and critical appraisal of peer-reviewed scientific papers.Sci Total Environ. 2010 Feb 1;408(5):999-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.003. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Sci Total Environ. 2010. PMID: 19945151
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Launay V. Caron A. Noirbent G. Gigmes D. Dumur F. Lalevée J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2006324.
-
- Ding W. Liu H. Li S. Remón J. Pang X. Ding Z. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022;10:17346–17354.
-
- Karadag R. J. Nat. Fibers. 2023;20:2162187.
-
- Al Fahad M. A., Ahamed R., Ahmed T., Jahan N., Mia R., Toki G. F. I., Mahmud S. T. and Niloy K. K., Renewable Dyes and Pigments, 2024, pp. 165–175
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

