Smartphone Photography in Plastic Surgery: Advancements, Ethics, and Best Practices
- PMID: 40762004
- PMCID: PMC12318659
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojaf065
Smartphone Photography in Plastic Surgery: Advancements, Ethics, and Best Practices
Abstract
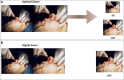
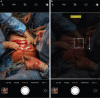
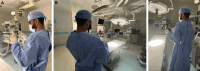
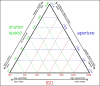
The extensive integration of smartphone photography has tremendously influenced plastic surgery, providing unmatched convenience, accessibility, and image quality. This comprehensive review explores the various applications of smartphone technology in the care of plastic surgery patients, from preoperative planning to postoperative monitoring. It emphasizes sophisticated smartphone camera capabilities and the potential for artificial intelligence-driven applications. However, using smartphones gives rise to noteworthy ethical considerations, requiring the implementation of solid regulations, adherence to guidelines, and personnel training to guarantee patient privacy and data security. This article is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals seeking to integrate smartphone photography into their practices while navigating the complex ethical landscape of digital imaging in healthcare. Level of Evidence: 5 (Risk).
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of prediction models for screening depression and anxiety using smartphone and wearable-based digital phenotyping: protocol for the Smartphone and Wearable Assessment for Real-Time Screening of Depression and Anxiety (SWARTS-DA) observational study in Korea.BMJ Open. 2025 Jun 20;15(6):e096773. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096773. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40541438 Free PMC article.
-
Be smart and use smartphones for telemedicine: narrative review.Mhealth. 2025 May 7;11:39. doi: 10.21037/mhealth-24-71. eCollection 2025. Mhealth. 2025. PMID: 40755939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smartphone and tablet self management apps for asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 27;2013(11):CD010013. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010013.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24282112 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Digital Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Healthcare: A Narrative Review.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Jul 31;27(1):119. doi: 10.1007/s11886-025-02270-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40742604 Review.
References
-
- Rowley M. Cabinet of art and medicine. Published January 30, 2016. Accessed January 30, 2016. http://www.artandmedicine.com/biblio/authors/Fox2.html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
