KLF7 orchestrates hippocampal development through neurogenesis and Draxin-mediated neuronal migration
- PMID: 40762575
- PMCID: PMC12377812
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.204718
KLF7 orchestrates hippocampal development through neurogenesis and Draxin-mediated neuronal migration
Abstract
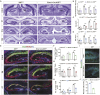
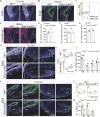
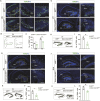
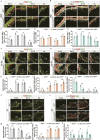
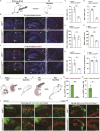
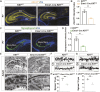
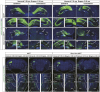
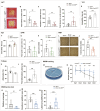
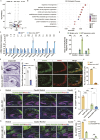
The hippocampus, a brain region that is crucial for cognitive learning, memory and emotional regulation, undergoes its primary development during embryonic and early postnatal stages. Krüppel-like factor 7 (KLF7), a transcription factor associated with autism spectrum disorder and intellectual developmental disorders, plays a pivotal role in brain development. In this study, we investigated the role of KLF7 in hippocampal development using conditional knockout mice [Emx1-Cre;Klf7Flox(F)/F]. We found that KLF7 deletion in hippocampal progenitors resulted in significant hippocampal shrinkage, disrupting neurogenesis, neuronal differentiation and migration. KLF7 mutant mice exhibited abnormal neuronal projections, anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, and memory impairments. Transcriptomic profiling identified Draxin, a neural chemorepellent, as a key downstream target of KLF7. Remarkably, overexpression of Draxin rescued dentate gyrus granule cell migration defects in KLF7 mutant mice. These findings demonstrate that KLF7 is essential for proper hippocampal development and function, regulating neuronal migration through Draxin. This study provides mechanistic insights into the neurological deficits associated with KLF7 pathogenic variants and highlights potential therapeutic targets for neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Draxin; Hippocampus; Krüppel-like factor 7; Mouse; Neurogenesis; Neuronal migration; Neuronal projections.
© 2025. Published by The Company of Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Alexandre, V., Walz, R., Bianchin, M. M., Velasco, T. R., Terra-Bustamante, V. C., Wichert-Ana, L., Araújo, D., Machado, H. R., Assirati, J. A., Carlotti, C. G.et al. (2006). Seizure outcome after surgery for epilepsy due to focal cortical dysplastic lesions. Seizure-Eur. J. Epilep. 15, 420-427. 10.1016/j.seizure.2006.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angevine, J. B.Jr. (1965). Time of neuron origin in the hippocampal region. An autoradiographic study in the mouse. Exp. Neurol. Suppl. Suppl. 2, 1-70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

