Correlation of Income Instability With 12 Non-Communicable Disease Risks in Korea: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 40762595
- PMCID: PMC12322588
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e180
Correlation of Income Instability With 12 Non-Communicable Disease Risks in Korea: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Due to the lack of comprehensive longitudinal studies examining the impact of long-term volatility on health issues, existing research primarily focused on income levels rather than fluctuation. Thus, we aimed to investigate the relationship between income instability and a range of physical health conditions using an extensive longitudinal dataset.
Methods: This study utilized data from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Ansan-Anseong cohort (2001-2022), which includes valuable confounding factors such as demographic, socioeconomic, lifestyle, and clinical factors. Income volatility was calculated as the intra-individual standard deviation of income changes across study waves. A Cox proportional hazards model was employed to assess correlations between income volatility and the risk of 12 non-communicable diseases (NCDs; hypertension, myocardial infarction [MI], coronary artery disease [CAD], cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, gout, gastric disease, renal disease, arthritis, allergic disease, and asthma).
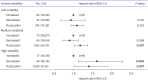
Results: A total of 9,185 participants (mean age, 52.21; male, 47.59%) were analyzed. In the fully adjusted model, medium volatility was correlated with a higher disease risk (hazard ratio, 1.14; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.21), as similar to high volatility (1.09; 1.03-1.16). The highest risk was observed in individuals experiencing income decreases (1.61; 1.13-2.28). All health conditions examined in this study showed an increased risk correlated with higher income volatility as follows: hypertension (1.13; 1.03-1.25); MI (2.15; 1.33-3.48); CAD (1.37; 1.04-3.48); cerebrovascular disease (1.69; 1.21-2.37); hyperlipidemia (1.14; 1.01-1.28); gout (2.11; 1.12-3.95); gastric disease (1.15; 1.01-1.32); renal disease (2.28; 1.22-4.25); arthritis (1.33; 1.04-1.70); allergic disease (1.54; 1.16-2.03); asthma (1.67; 1.04-1.67).
Conclusion: Income volatility, particularly income decreases and fluctuations, is significantly correlated with higher risk of chronic NCDs in South Korea. These findings underscore the need to develop interventions to mitigate financial instability, thereby improving public health outcomes.
Keywords: Disease Risk; Income Instability; Korea; Non-communicable Disease.
© 2025 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Kivimäki M, Batty GD, Pentti J, Shipley MJ, Sipilä PN, Nyberg ST, et al. Association between socioeconomic status and the development of mental and physical health conditions in adulthood: a multi-cohort study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(3):e140–e149. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

