Blood pressure and vascular function response to maximal graded exercise tests in young men with masked hypertension
- PMID: 40763085
- PMCID: PMC12404028
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00007.2025
Blood pressure and vascular function response to maximal graded exercise tests in young men with masked hypertension
Abstract
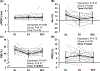
Individuals with masked hypertension have out-of-office blood pressure (BP) readings in the hypertensive range, but office BP readings below the hypertensive cutoff, making masked hypertension less likely to be diagnosed. The aim of this study was to determine whether in-laboratory measurements of BP and vascular function in response to exercise can serve as indicators of masked hypertension in young adults. Thirty-three young men with office BP <130/80 mmHg, free of smoking and clinical diseases, were included in this study. All participants underwent 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring for BP classification, as well as in-laboratory BP and vascular assessments at rest and after a maximal graded exercise test on a cycle ergometer. These assessments included peripheral and central BP, arterial stiffness, wave reflection, and endothelial function. Compared to participants without masked hypertension (CON; n = 17), those with masked hypertension (MH; n = 16) had a higher level of 24-h, daytime, and nighttime systolic BP (P ≤ 0.005), but similar office BP (P ≥ 0.5). No differences between groups were found in peripheral BP and vascular function measurements at baseline (P ≥ 0.2) and in response to exercise (P ≥ 0.2 for group by time interaction effects). Although central systolic BP at rest was similar between groups (P = 0.17), MH had a higher marginal mean of central systolic BP from resting, following exercise, and during recovery (MH vs. CON: 113 ± 2 vs. 108 ± 2 mmHg, P = 0.047 for group effect). These findings suggest that in young men, masked hypertension may be associated with an elevated central systolic BP, which could be induced by exercise.NEW & NOTEWORTHY We show for the first time that in young men, peripheral blood pressure (BP) and vascular function in response to maximal graded exercise tests were not different between individuals with and without masked hypertension. On the other hand, in young men, masked hypertension may be associated with an elevated central systolic BP, which could be induced by exercise.
Keywords: acute exercise; ambulatory blood pressure; cardiovascular risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
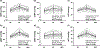
References
-
- Stergiou GS, Asayama K, Thijs L, Kollias A, Niiranen TJ, Hozawa A, Boggia J, Johansson JK, Ohkubo T, Tsuji I, Jula AM, Imai Y, Staessen JA, and International Database on HbpirtCOI. Prognosis of white-coat and masked hypertension: International Database of HOme blood pressure in relation to Cardiovascular Outcome. Hypertension 63: 675–682, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher GF, Ades PA, Kligfield P, Arena R, Balady GJ, Bittner VA, Coke LA, Fleg JL, Forman DE, Gerber TC, Gulati M, Madan K, Rhodes J, Thompson PD, Williams MA, American Heart Association Exercise CR, Prevention Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology CoNPA, Metabolism CoC, Stroke N, Council on E, and Prevention. Exercise standards for testing and training: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 128: 873–934, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Manolio TA, Burke GL, Savage PJ, Sidney S, Gardin JM, and Oberman A. Exercise blood pressure response and 5-year risk of elevated blood pressure in a cohort of young adults: the CARDIA study. Am J Hypertens 7: 234–241, 1994. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

