Modification of belantamab mafodotin dosing to balance efficacy and tolerability in the DREAMM-7 and DREAMM-8 trials
- PMID: 40763276
- PMCID: PMC12657289
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025016949
Modification of belantamab mafodotin dosing to balance efficacy and tolerability in the DREAMM-7 and DREAMM-8 trials
Abstract
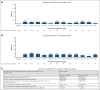
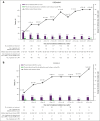
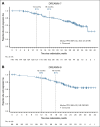
Belantamab mafodotin (belamaf) combined with standard therapies demonstrated significant progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival benefits in DREAMM-7 and PFS benefit in DREAMM-8 in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Belamaf dose modifications managed adverse events, including belamaf-related ocular events. Ocular events included ocular adverse reactions (eg, dry eyes, photophobia, eye irritation) and protocol-mandated ophthalmic examination findings. Protocol-recommended dose modifications for ocular events were driven by ophthalmic examination findings and included belamaf dose delays until resolution and reductions. We used descriptive analyses to evaluate the impact of dose modifications on managing ocular events and treatment efficacy. In patients with normal baseline vision who were receiving treatment, dose modifications extended belamaf dosing intervals to a median of 8 to 12 weeks by 9 months; the prevalences of reduced vision to bilateral 20/50 or worse and ocular adverse reactions were highest in the first 3 months and remained low at later time points. The median time to resolution after grade ≥2 ophthalmic examination findings was 12 weeks. Rates of belamaf discontinuations due to ocular events were low. Almost all responders (partial response or better) required dose modifications. Most patients achieved a response before an extended (>2 cycles) dose delay; most who had not, subsequently achieved or deepened their response. In DREAMM-7 and DREAMM-8, the median PFS in patients with ≥1 dose delay of ≥12 weeks was 36.6 months and not reached, respectively. Ocular events were common but effectively managed with dose modifications, allowing for patients to remain on treatment and derive robust efficacy benefit. The trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT04246047 (DREAMM-7) and #NCT04484623 (DREAMM-8).
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.V.M. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), GSK, Sanofi, AbbVie, Kite, Stemline, and Pfizer; and participation on a data safety monitoring or advisory board for Janssen, BMS, Amgen, Sanofi, GSK, Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, Kite, and Stemline. S.T. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Amgen, GSK, Janssen, Pfizer, and Sanofi; consulting or advisory role at BMS, GSK, and Roche; and research funding from Amgen, BMS, Genentech, GSK, Janssen, K36 Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Roche. M.B. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from BMS and Janssen; and consulting or advisory role at GSK, Takeda, Amgen, Janssen, and Menarini. S.D. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Amgen, GSK, Janssen, and Takeda. T.J. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events and/or research grants from Sanofi, Janssen, BMS, Pfizer, and GSK. C.W. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, and speakers’ bureaus from AstraZeneca, CSL, GSK, Alexion, Bayer, and Drivetime Radio; and was the education and planning committee chair for the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2024 Congress. P.J.H. reports participation on a data safety monitoring or advisory board for the Australasian Leukaemia & Lymphoma Group trials; unpaid leadership or fiduciary roles in advisory boards for Antengene, Gilead, iTeos Therapeutics, Janssen, and Pfizer; and research and medical writing support from Novartis. V.V. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; consulting or advisory role for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Oncology, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda; payment or honoraria for speakers bureaus from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Biocad, BMS, Janssen, Merck & Co, Inc, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; and travel, accommodations, and expenses from AstraZeneca. I.S. reports consulting fees from BMS, Amgen, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, Sanofi, and GSK; honoraria from Amgen, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, BMS, and Sanofi; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Janssen-Cilag, BMS, and Sanofi; and participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, Sanofi, and GSK. J.R. reports consulting fees from GSK, Johnson & Johnson, and Sanofi; honoraria from Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, BMS, Sanofi, and GSK; support for attending meetings and/or travel from Johnson & Johnson and Sanofi; and participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for GSK, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, BMS, and Pfizer. C.C. reports stock or stock options in GSK; and advisory board speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, BeiGene, BMS, Glycomimetics, GSK, Immunogen, Janssen, Jazz, Karyopharm, Menarini-Stemline, Oncopeptides, Pfizer, Sanofi, Servier, Stemline, and Takeda. K.S. reports honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Sanofi, and BMS. R.R., Z.W., H.B., J.W., X.L.Z., E.L., L.E., P.P., and P.M. report employment and/or stock or stock options at GSK. A.P.-J. and N.S. report employment and/or stock or stock options at GSK; and travel support from GSK. J.B.O. reports issued or pending patents and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, educational events, or travel support from GSK; and employment and/or stock or stock options at GSK. V.H. reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Janssen, Sanofi, Pfizer, and Takeda; and participation on a data safety monitoring or advisory board for BMS, GSK, Janssen, Kite, Regeneron, and Sanofi. M.A.D. reports honoraria from Amgen, Sanofi, Regeneron, Menarini, Takeda, GSK, BMS, Janssen, BeiGene, Swixx, and AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for X.L.Z. is ONO PHARMA USA, Waltham, MA.
Figures



References
-
- Hungria V, Robak P, Hus M, et al. Belantamab mafodotin, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(5):393–407. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Beksac M, Pour L, et al. Belantamab mafodotin, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(5):408–421. - PubMed
-
- Hungria V, Robak P, Hus M. 7-10 December 2024. Belantamab mafodotin, bortezomib, and dexamethasone vs daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: overall survival analysis and updated efficacy outcomes of the phase 3 DREAMM-7 trial. Paper presented at: 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition. San Diego, CA.
-
- Popat R, Nooka A, Stockerl-Goldstein K, et al. DREAMM-6: safety, tolerability and clinical activity of belantamab mafodotin (belamaf) in combination with bortezomib/dexamethasone (bordex) in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) [abstract] Blood. 2020;136(suppl 1):19–20.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

