Epigenetic liquid biopsies reveal endothelial turnover and erythropoiesis in asymptomatic COVID-19
- PMID: 40763987
- PMCID: PMC12326330
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202503417
Epigenetic liquid biopsies reveal endothelial turnover and erythropoiesis in asymptomatic COVID-19
Abstract
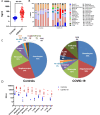
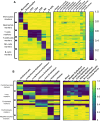
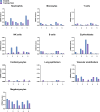
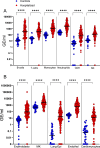
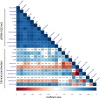
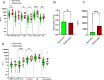
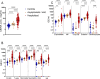
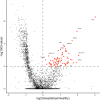
Understanding the full spectrum of tissues affected by SARS-CoV-2 is crucial for deciphering the heterogeneous clinical course of COVID-19. We analyzed DNA methylation and histone modifications in circulating chromatin to assess cell type-specific turnover in patients ranging from asymptomatic to severe cases, in relation to clinical outcomes. Severe COVID-19 was marked by a massive elevation of circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from lung epithelium, cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelium, and erythroblasts, indicating increased cell death or turnover. The immune response was reflected by elevated B-cell and monocyte/macrophage cfDNA and an interferon response before cfDNA release. Strikingly, monocyte/macrophage cfDNA (but not monocyte counts), as well as lung epithelial and endothelial cfDNA, predicted clinical deterioration and duration of hospitalization. Asymptomatic patients had elevated immune cfDNA but no evidence of pulmonary or cardiac damage. Surprisingly, these patients showed elevated endothelial and erythroblast cfDNA, suggesting subclinical vascular and erythrocyte turnover are universal features of COVID-19, independent of disease severity. Epigenetic liquid biopsies provide a noninvasive means of monitoring COVID-19 patients and reveal subclinical vascular damage and red blood cell turnover.
© 2025 Ben-Ami et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Supported in part by GRAIL, Inc., G Cann is an employee and shareholder at GRAIL, Inc. I Sharkia and N Friedman are shareholders and/or founders at Senseera, Inc. N Loyfer, T Kaplan, B Glaser, R Shemer, and Y Dor have filed patents on cfDNA analysis technology. The remaining authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
cfDNA methylation detection as potential liquid biopsy of multiple organ injury in myocarditis patients.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 Jun 19;17(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01914-z. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 40537817 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free epigenomes enhanced fragmentomics-based model for early detection of lung cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Feb;15(2):e70225. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70225. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39909829 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 2;9(9):CD013825. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013825.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34473343 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
