Automated ultrasound system ARTHUR V.2.0 with AI analysis DIANA V.2.0 matches expert rheumatologist in hand joint assessment of rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 40764087
- PMCID: PMC12336591
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2025-005805
Automated ultrasound system ARTHUR V.2.0 with AI analysis DIANA V.2.0 matches expert rheumatologist in hand joint assessment of rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
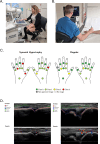
Objective: To evaluate the agreement and repeatability of an automated robotic ultrasound system (ARTHUR V.2.0) combined with an AI model (DIANA V.2.0) in assessing synovial hypertrophy (SH) and Doppler activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, using an expert rheumatologist's assessment as the reference standard.
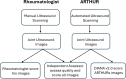
Methods: 30 RA patients underwent two consecutive ARTHUR V.2.0 scans and rheumatologist assessment of 22 hand joints, with the rheumatologist blinded to the automated system's results. Images were scored for SH and Doppler by DIANA V.2.0 using the EULAR-OMERACT scale (0-3). The agreement was evaluated by weighted Cohen's kappa, percent exact agreement (PEA), percent close agreement (PCA) and binary outcomes using Global OMERACT-EULAR Synovitis Scoring (healthy ≤1 vs diseased ≥2). Comparisons included intra-robot repeatability and agreement with the expert rheumatologist and a blinded independent assessor.
Results: ARTHUR successfully scanned 564 out of 660 joints, corresponding to an overall success rate of 85.5%. Intra-robot agreement for SH: PEA 63.0%, PCA 93.0%, binary 90.5% and for Doppler, PEA 74.8%, PCA 93.7%, binary 88.1% and kappa values of 0.54 and 0.49. Agreement between ARTHUR+DIANA and the rheumatologist: SH (PEA 57.9%, PCA 92.9%, binary 87.3%, kappa 0.38); Doppler (PEA 77.3%, PCA 94.2%, binary 91.2%, kappa 0.44) and with the independent assessor: SH (PEA 49.0%, PCA 91.2%, binary 80.0%, kappa 0.39); Doppler (PEA 62.6%, PCA 94.4%, binary 88.1%, kappa 0.48).
Conclusions: ARTHUR V.2.0 and DIANA V.2.0 demonstrated repeatability on par with intra-expert agreement reported in the literature and showed encouraging agreement with human assessors, though further refinement is needed to optimise performance across specific joints.
Keywords: Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Machine Learning; Ultrasonography.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SAJ and TRS are cofounders of Ropca Aps, developing AI and producing the automated ultrasound scanning system called ARTHUR. ARTHUR’s AI cannot currently assess osteophyte severity. AC is a full-time employee of Ropca Aps.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and ultrasound optimization in rheumatoid arthritis for patients in sustained remission, can it work as a new optimization tool?J Ultrasound. 2025 Mar;28(1):81-87. doi: 10.1007/s40477-024-00963-z. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Ultrasound. 2025. PMID: 39424691 Clinical Trial.
-
Occupational therapist-led versus rheumatologist-led care in people with hand osteoarthritis in Norway: an open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled, non-inferiority trial.Lancet Rheumatol. 2025 Aug;7(8):e533-e543. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00040-2. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Lancet Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40513596 Clinical Trial.
-
Inter- and intra-observer agreement of high-resolution ultrasonography and power Doppler in assessment of joint inflammation and bone erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Jan;33(1):173-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-2297-9. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 22274131
-
What is the added value of ultrasound joint examination for monitoring synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis and can it be used to guide treatment decisions? A systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Apr;22(20):1-258. doi: 10.3310/hta22200. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 29712616 Free PMC article.
-
Automated devices for identifying peripheral arterial disease in people with leg ulceration: an evidence synthesis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Aug;28(37):1-158. doi: 10.3310/TWCG3912. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39186036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Agostino M-A, Terslev L, Aegerter P, et al. Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: a EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 1: definition and development of a standardised, consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open. 2017;3:e000428. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000428. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Terslev L, Naredo E, Aegerter P, et al. Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: a EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 2: reliability and application to multiple joints of a standardised consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open. 2017;3:e000427. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
