Large-scale genome-wide analyses with proteomics integration reveal novel loci and biological insights into frailty
- PMID: 40764432
- PMCID: PMC12350161
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00925-y
Large-scale genome-wide analyses with proteomics integration reveal novel loci and biological insights into frailty
Abstract
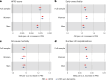
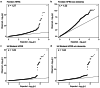
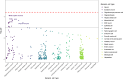
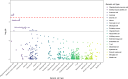
Frailty is a clinically relevant phenotype with notable gaps in our understanding of its etiology. Using the Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) to define frailty, we performed a genome-wide association study in FinnGen (N = 500,737), replicated the results in the UK Biobank (N = 407,463) and performed a meta-analysis. We prioritized genes through colocalization with expression, splicing and protein quantitative trait loci and proteomics integration. We identified 53 independent lead variants associated with frailty (P < 5 × 10-8), of which 45 were novel and not previously reported in the GWAS Catalog. Replication at the individual variant and polygenic risk score of the HFRS (P = 1.86 × 10-522) levels and meta-analysis largely confirmed the findings. Colocalization analysis supported a causal role for several genes, including CHST9, C6orf106 (ILRUN), KHK, MET, APOE, CGREF1 and PPP6C. Additionally, plasma levels of MET, CGREF1 and APOE were associated with HFRS. Our results reveal new genetic contributions to frailty and shed light on its biological basis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kojima, G., Iliffe, S. & Walters, K. Frailty index as a predictor of mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing47, 193–200 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Theou, O., Brothers, T. D., Mitnitski, A. & Rockwood, K. Operationalization of frailty using eight commonly used scales and comparison of their ability to predict all-cause mortality. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc.61, 1537–1551 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

