Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of prediabetes and diabetes mellitus in older adults: findings from Iranian STEPS surveys (2016 and 2021)
- PMID: 40764559
- PMCID: PMC12326772
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-23654-8
Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of prediabetes and diabetes mellitus in older adults: findings from Iranian STEPS surveys (2016 and 2021)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of prediabetes and diabetes mellitus in older adults: findings from Iranian STEPS surveys (2016 and 2021).BMC Public Health. 2025 Oct 17;25(1):3517. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-24762-1. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 41107812 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a significant public health concern, particularly among older adults who face an elevated risk of complications and increased mortality. This study assessed overtime changes in the prevalence, awareness, treatment coverage, and glycemic control of DM in Iranian adults aged 60 and older.
Methods: This is a nationwide repeated cross-sectional study based on data from the 2016 and 2021 STEPwise Approach to Non-communicable Disease Risk Factor Surveillance (STEPS), the most recent surveys conducted across all provinces of Iran. We reported prevalence estimates as weighted percentages with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Logistic regression was used to evaluate the association between selected demographic and health characteristics and diabetes mellitus (DM). All analyses were performed using R statistical software version 4.0.5.
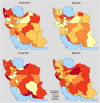
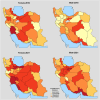
Results: From 2016 to 2021, the prevalence of prediabetes increased from 23.86 to 28.96% in males and from 22.86 to 30.86% in females, while DM prevalence rose from 19.37 to 25.43% in males and from 26.22 to 30.26% in females. In 2016, DM awareness was 74.47% in males and 82.19% in females, and in 2021, it was 71.20% in males and 78.73% in females. Treatment coverage was 60.18% in males and 67.63% in females in 2016, and 63.71% in males and 71.14% in females in 2021. Glycemic control was 59.77% in males and 57.98% in females in 2016, and 55.96% in males and 53.66% in females in 2021. Obesity significantly increased the odds of DM (odds ratio (OR) 1.97, p < 0.001), while being underweight (OR 0.21, p < 0.001) and having sufficient physical activity (OR 0.77, p = 0.02) were protective factors.
Conclusion: The findings from the 2016 and 2021 STEPS surveys indicate a rising burden of prediabetes and DM among older adults in Iran, particularly among females. Although awareness and treatment coverage were high, optimal glycemic control remains a challenge, emphasizing the need to improve access to healthcare resources and develop tailored community-based interventions.
Keywords: Aged; Awareness; Control; Diabetes; Prevalence; Risk factors; Treatment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study received approval from the Research Ethics Committees of the Endocrine & Metabolism Research Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences (IR.TUMS.EMRI.REC.1403.053) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants were informed about the survey’s methods and objectives, and written informed consent was obtained prior to their enrollment in the survey. No personally identifiable information was included in the research data, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical