Isofloridoside: a novel inhibitor of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation and glucosyltransferase activity
- PMID: 40764584
- PMCID: PMC12326583
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-025-07408-8
Isofloridoside: a novel inhibitor of Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation and glucosyltransferase activity
Abstract
Objective: Isofloridoside, a galactose-containing heteroside derived from marine red algae, has potential applications as a sweetener because it can activate the sweetness receptors T1R2/T1R3. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of isofloridoside on the growth and sucrose-dependent biofilm formation of the cariogenic bacterium Streptococcus mutans, to evaluate its potential as a caries-preventing agent.
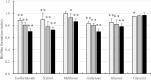
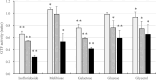
Results: The results showed that S. mutans did not grow when isofloridoside was the sole carbon source. Isofloridoside inhibited sucrose-dependent biofilm formation by S. mutans in a concentration-dependent manner, similar to galactose and glucose, but unlike melibiose and galactose-containing disaccharides. Biofilm inhibition induced by isofloridoside was associated with inhibition of glucosyltransferase activity. Isofloridoside exhibited biofilm inhibition comparable to xylitol, an alternative sugar known to inhibit biofilm formation. The differential effects of isofloridoside and melibiose on biofilm formation may result from the structural differences that affect their interactions with S. mutans enzymes. These findings highlight the potential of galactose and its polysaccharides as regulators of S. mutans biofilm formation, and suggest that isofloridoside is a promising alternative sweetener for caries prevention.
Keywords: Streptococcus mutans; Alternative sweetener; Biofilm formation; Dental caries; Galactose; Glucosyltransferase (GTF); Isofloridoside.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gasmi Benahmed A, Gasmi A, Arshad M, Shanaida M, Lysiuk R, Peana M, et al. Health benefits of xylitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;104:7225–37. - PubMed
-
- Marttinen AM, Ruas-Madiedo P, Hidalgo-Cantabrana C, Saari MA, Ihalin RA, Söderling EM. Effects of xylitol on xylitol-sensitive versus xylitol-resistant Streptococcus mutans strains in a three-species in vitro biofilm. Curr Microbiol. 2012;65:237–43. - PubMed
-
- Li Y-X, Li Y, Lee S-H, Qian Z-J, Kim S-K. Inhibitors of oxidation and matrix metalloproteinases, floridoside, and D-isofloridoside from marine red alga Laurencia undulata. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58:578–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

