Role of extracellular vesicle-carried ncRNAs in the interactive 'dialogue' within the brain and beyond: emerging theranostic epigenetic modifiers in brain-derived nanoplatforms
- PMID: 40764607
- PMCID: PMC12323186
- DOI: 10.1186/s40035-025-00502-8
Role of extracellular vesicle-carried ncRNAs in the interactive 'dialogue' within the brain and beyond: emerging theranostic epigenetic modifiers in brain-derived nanoplatforms
Abstract
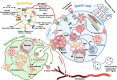
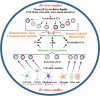
Proper brain function and overall health critically rely on the bidirectional communications among cells in the central nervous system and between the brain and other organs. These interactions are widely acknowledged to be facilitated by various bioactive molecules present in the extracellular space and biological fluids. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are an important source of the human neurosecretome and have emerged as a novel mechanism for intercellular communication. They act as mediators, transferring active biomolecules between cells. The fine-tuning of intracellular trafficking processes is crucial for generating EVs, which can significantly vary in composition and content, ultimately influencing their fate and function. Increasing interest in the role of EVs in the nervous system homeostasis has spurred greater efforts to gain a deeper understanding of their biology. This review aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of brain-derived small EVs based on their epigenetic cargo, highlighting the importance of EV-encapsulated non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the intercellular communication in the brain. We comprehensively summarize experimentally confirmed ncRNAs within small EVs derived from neurons, astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes across various neuropathological conditions. Finally, through in-silico analysis, we present potential targets (mRNAs and miRNAs), hub genes, and cellular pathways for these ncRNAs, representing their probable effects after delivery to recipient cells. In summary, we provide a detailed and integrated view of the epigenetic landscape of brain-derived small EVs, emphasizing the importance of ncRNAs in brain intercellular communication and pathology, while also offering prognostic insights for future research directions.
Keywords: Brain; CirRNA; Epigenetic; Exosomes; LncRNA; MiRNAs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Raposo G, Stahl PD. Extracellular vesicles: a new communication paradigm? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(9):509–10. - PubMed
-
- Karampoga A, Tzaferi K, Koutsakis C, Kyriakopoulou K, Karamanos NK. Exosomes and the extracellular matrix: a dynamic interplay in cancer progression. Int J Dev Biol. 2022;66(1-2–3):97–102. - PubMed
-
- Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

