SERBP1-PCIF1 complex-controlled m6Am modification in glutamatergic neurons of the primary somatosensory cortex is required for neuropathic pain in mice
- PMID: 40764612
- PMCID: PMC12326004
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62565-5
SERBP1-PCIF1 complex-controlled m6Am modification in glutamatergic neurons of the primary somatosensory cortex is required for neuropathic pain in mice
Abstract
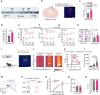
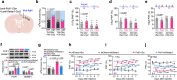
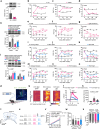
Nerve injury-induced changes in pain-associated genes contribute to genesis of neuropathic pain and comorbid anxiety. Phosphorylated CTD interacting factor-1 (PCIF1)-triggered N6, 2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) mRNA modification represents an additional layer of gene regulation. However, the role of PCIF1 in these disorders is elusive. Here, we report PCIF1 is increased in glutamatergic neurons of the hindlimb region of the primary somatosensory cortex in mouse with neuropathic pain and anxiety, but not inflammatory pain or anxiety alone. Serpine-1 mRNA-binding protein-1 (SERBP1) is identified as a PCIF1 cofactor, their complex mediates m6Am deposition onto mRNA. Blocking SERBP1-PCIF1 upregulation in glutamatergic neurons of the hindlimb region of the primary somatosensory cortex abolishes m6Am gain on maf1 homolog, negative regulator of RNA polymerase III (Maf1), elevates MAF1 protein, and mitigates neuropathic pain and anxiety. Conversely, mimicking this increase adds m6Am onto Maf1, reduces MAF1, and induces comorbidity symptoms. These findings highlight the significance of m6Am in neuropathic pain-anxiety comorbidity and identify SERBP1-PCIF1 in glutamatergic neurons of the hindlimb region of the primary somatosensory cortex as a potential therapeutic target.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The transcription factor Y-box binding protein 3 contributes to mechanical allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in trigeminal neuralgia by transcriptionally triggering period circadian regulator 1 in primary sensory neurons.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;320(Pt 4):146097. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146097. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40683511
-
m6Am Methyltransferase PCIF1 Regulates Periodontal Inflammation.J Dent Res. 2024 Oct;103(11):1130-1140. doi: 10.1177/00220345241271078. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 39290151
-
NaHS alleviates neuropathic pain in mice by inhibiting IL-17-mediated dopamine (DA) neuron necroptosis in the VTA.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Jan;220:111168. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111168. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39672209
-
Tramadol for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 15;6(6):CD003726. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003726.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28616956 Free PMC article.
-
Venlafaxine for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 23;2015(8):CD011091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26298465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Hecke, O., Austin, S. K., Khan, R. A., Smith, B. H. & Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain155, 654–662 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Attal, N., Bouhassira, D. & Colvin, L. Advances and challenges in neuropathic pain: a narrative review and future directions. Br. J. Anaesth.131, 79–92 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Li, X. Y. et al. Alleviating neuropathic pain hypersensitivity by inhibiting PKMzeta in the anterior cingulate cortex. Science330, 1400–1404 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Jin, Y. et al. A somatosensory cortex input to the caudal dorsolateral striatum controls comorbid anxiety in persistent pain. Pain161, 416–428 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

