Small-molecule CGRP antagonist atogepant does not affect cortical spreading depression susceptibility in rats
- PMID: 40764901
- PMCID: PMC12326636
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-025-02127-8
Small-molecule CGRP antagonist atogepant does not affect cortical spreading depression susceptibility in rats
Abstract
Background: Atogepant is a small-molecule non-competitive calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist efficacious in preventing episodic migraine. Cortical spreading depolarization (CSD) is a slowly propagating depolarization wave underlying migraine aura. We investigated whether the efficacy of atogepant in migraine is mediated by CSD suppression.
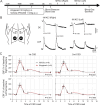
Method: We used Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 28 males, 28 females) to determine the electrical stimulation intensity threshold for CSD induction and the frequency of CSDs induced by continuous topical 1 M KCl application sequentially in the same animal, using intracortical glass microelectrodes under isoflurane anesthesia and full systemic physiological monitoring, including arterial blood pressure and blood gases. In a separate cohort, we disrupted the BBB by inducing three CSDs in the contralateral hemisphere using 1 M KCl daily for 2 days before CSD susceptibility testing. Both cohorts received atogepant (30 mg/kg, once daily oral gavage) or vehicle for four days. CSD susceptibility was examined 1 h after the last atogepant dose.
Results: Atogepant did not affect the CSD threshold, frequency, propagation speed, amplitude, or duration compared with vehicle, either without or with preceding CSDs. Systemic physiological parameters did not differ between groups.
Conclusions: These data suggest that atogepant efficacy in migraine is not mediated via CSD suppression, even when BBB permeability is increased.
Keywords: Atogepant; Blood-brain barrier; CGRP; Migraine; Spreading depression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: Pradeep Banerjee is an employee of AbbVie, which provided atogepant for this study. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral atogepant mitigates spreading depolarization-induced pain and anxiety behavior in mice.J Headache Pain. 2025 Aug 21;26(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02125-w. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40841621 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive drug treatments for adults with chronic migraine: a systematic review with economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(63):1-329. doi: 10.3310/AYWA5297. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39365169 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of lacosamide on cortical spreading depolarization in mice.J Headache Pain. 2025 Jul 16;26(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02099-9. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40670944 Free PMC article.
-
One-month atogepant treatment induces rapid changes in delta-band functional connectivity in migraine: an HD-EEG study.J Headache Pain. 2025 Jul 30;26(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s10194-025-02115-y. J Headache Pain. 2025. PMID: 40739615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insight into atogepant mechanisms of action in migraine prevention.Brain. 2024 Aug 1;147(8):2884-2896. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae062. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38411458 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

