Clinical utility of two-dimensional shear wave elastography in two dogs with presumptive toxic hepatopathy
- PMID: 40765227
- PMCID: PMC12329062
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.25083
Clinical utility of two-dimensional shear wave elastography in two dogs with presumptive toxic hepatopathy
Abstract
Importance: Shear wave elastography (SWE) is a non-invasive ultrasound technique for assessing tissue stiffness. This study examined the clinical utility of two-dimensional SWE (2D-SWE) in two dogs diagnosed with presumptive toxic hepatopathy.
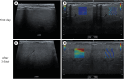
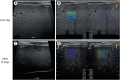
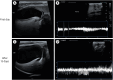
Case presentation: The first case involved a 9-year-old Pompitz that presented with anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea following garlic and onion ingestion. Laboratory tests revealed anemia, elevated liver enzyme levels, and diabetic ketoacidosis. Ultrasonography demonstrated increased hepatic echogenicity and elevated SWE values. Despite intensive treatment, the dog's condition deteriorated, with progressive increases in liver enzyme levels and SWE values, resulting in euthanasia. The second case involved a 1-year-old Maltipoo that presented vomiting, depression, and abdominal pain, with no reported history. Laboratory findings indicated elevated liver enzyme and bile acid levels. Ultrasonography revealed increased hepatic echogenicity and SWE values. Following treatment for acute toxic hepatopathy, the dog exhibited significant improvement within 3 days, with normalization of hepatic echogenicity, SWE values, and liver enzyme levels.
Conclusions and relevance: These cases demonstrate the clinical relevance of 2D-SWE in assessing hepatic damage, tracking therapeutic response, and informing prognosis in presumptive toxic hepatopathy.
Keywords: Ultrasonography; acute toxicity tests; dogs; liver; shear wave velocity.
© 2025 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shear wave elastography correlates with liver fibrosis scores in pediatric patients with liver disease.Pediatr Radiol. 2019 Dec;49(13):1742-1753. doi: 10.1007/s00247-019-04493-3. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Pediatr Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31418057
-
Utilization of Shear Wave Elastography in the Evaluation of Pediatric Liver Transplant: A Prospective Case-Controlled Study.Pediatr Transplant. 2025 Aug;29(5):e70120. doi: 10.1111/petr.70120. Pediatr Transplant. 2025. PMID: 40590071
-
Doppler ultrasound and 2D shear wave ultrasound elastography for liver fibrosis evaluation in Fontan-associated liver disease.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 5;25(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04151-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40764907 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of shear wave elastography in measuring placental stiffness for pre-eclampsia screening and diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025 Jun 23. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.70293. Online ahead of print. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2025. PMID: 40548415 Review.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Transient Elastography Versus Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Direct Comparison and a Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 17;2022:1960244. doi: 10.1155/2022/1960244. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36164448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larson MM. Ultrasound imaging of the hepatobiliary system and pancreas. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2016;46(3):453–480. - PubMed
-
- Kemp SD, Panciera DL, Larson MM, Saunders GK, Werre SR. A comparison of hepatic sonographic features and histopathologic diagnosis in canine liver disease: 138 cases. J Vet Intern Med. 2013;27(4):806–813. - PubMed
-
- Toom M, Saunders J, Duchateau L, de Rooster H, Devriendt N, Stock E. Evaluation of liver stiffness in a population of client owned healthy dogs using two-dimensional shear wave elastography: intraobserver reliability. Vlaams Diergeneeskd Tijdschr. 2023;92(2):66–74.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

