Arrestins as Possible Drug Targets
- PMID: 40765306
- PMCID: PMC12408197
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2025.079
Arrestins as Possible Drug Targets
Abstract
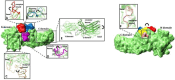
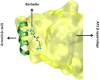
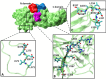
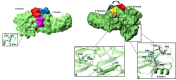
Out of at least 20,000 human proteins fewer than 700 are targeted by drugs. Arrestins regulate G protein-coupled receptors, the largest family of signaling proteins in animals, as well as many receptor-independent signaling pathways. Humans express four arrestin subtypes, two of which are ubiquitous and were already shown to serve as versatile hubs of cellular signaling. So far, arrestin proteins are not directly targeted by any drugs. Here we describe potential targets on arrestins and/or interacting proteins, possible approaches for the development of targeting compounds, expected biological outcomes, and possible research and therapeutic value of targeting the interactions of arrestins with receptors and other signaling and trafficking proteins.
Keywords: Arrestin; Cell signaling; Drug target; GPCR.
Figures

References
-
- Aydin Y., Böttke T., Lam J. H., Ernicke S., Fortmann A., Tretbar M., Zarzycka B., Gurevich V. V., Katritch V., Coin I. Structural details of a Class B GPCR-arrestin complex revealed by genetically encoded crosslinkers in living cells. Nat. Commun. 2023;14:1151. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36797-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beautrait A., Paradis J. S., Zimmerman B., Giubilaro J., Nikolajev L., Armando S., Kobayashi H., Yamani L., Namkung Y., Heydenreich F. M., Khoury E., Audet M., Roux P. P., Veprintsev D. B., Laporte S. A., Bouvier M. A new inhibitor of the beta-arrestin/AP2 endocytic complex reveals interplay between GPCR internalization and signalling. Nat. Commun. 2017;18:15054. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15054. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

